The crosstalk between m6A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators: a novel perspective in epigenetic remodeling
- PMID: 33754077
- PMCID: PMC7977459
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.54967
The crosstalk between m6A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators: a novel perspective in epigenetic remodeling
Abstract
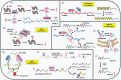
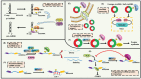
Epigenetic regulation involves a range of sophisticated processes which contribute to heritable alterations in gene expression without altering DNA sequence. Regulatory events predominantly include DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, histone modifications, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), and RNA modification. As the most prevalent RNA modification in eukaryotic cells, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation actively participates in the modulation of RNA metabolism. Notably, accumulating evidence has revealed complicated interrelations occurring between m6A and other well-known epigenetic modifications. Their crosstalk conspicuously triggers epigenetic remodeling, further yielding profound impacts on a variety of physiological and pathological processes, especially tumorigenesis. Herein, we provide an up-to-date review of this emerging hot area of biological research, summarizing the interplay between m6A RNA methylation and other epigenetic regulators, and highlighting their underlying functions in epigenetic reprogramming.
Keywords: DNA methylation; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); RNA modification; chromatin remodeling; histone modification; non-coding RNA (ncRNA).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Katada S, Imhof A, Sassone-Corsi P. Connecting threads: epigenetics and metabolism. Cell. 2012;148:24–8. - PubMed
-
- Xiang JF, Yang Q, Liu CX, Wu M, Chen LL, Yang L. N6-methyladenosines modulate A-to-I RNA editing. Mol Cell. 2018;69:126–35. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Zhu P, Ma S, Song J, Bai J, Sun F. et al. Chemical pulldown reveals dynamic pseudouridylation of the mammalian transcriptome. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11:592–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

