Niraparib with androgen receptor-axis-targeted therapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: safety and pharmacokinetic results from a phase 1b study (BEDIVERE)
- PMID: 33754187
- PMCID: PMC8149334
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-021-04249-7
Niraparib with androgen receptor-axis-targeted therapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: safety and pharmacokinetic results from a phase 1b study (BEDIVERE)
Abstract
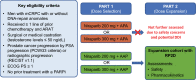
Purpose: To assess the safety and pharmacokinetics and determine the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) of niraparib with apalutamide or abiraterone acetate plus prednisone (AAP) in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
Methods: BEDIVERE was a multicenter, open-label, phase 1b study of niraparib 200 or 300 mg/day with apalutamide 240 mg or AAP (abiraterone acetate 1000 mg; prednisone 10 mg). Patients with mCRPC were previously treated with ≥ 2 lines of systemic therapy, including ≥ 1 androgen receptor-axis-targeted therapy for prostate cancer.
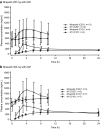
Results: Thirty-three patients were enrolled (niraparib-apalutamide, 6; niraparib-AAP, 27). No dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) were reported when combinations included niraparib 200 mg; five patients receiving niraparib 300 mg experienced DLTs [niraparib-apalutamide, 2/3 patients (66.7%); niraparib-AAP, 3/8 patients (37.5%)]. Although data are limited, niraparib exposures were lower when given with apalutamide compared with historical niraparib monotherapy exposures in patients with solid tumors. Because of the higher incidence of DLTs, the niraparib-apalutamide combination and niraparib 300 mg combination with AAP were not further evaluated. Niraparib 200 mg was selected as the RP2D with AAP. Of 19 patients receiving niraparib 200 mg with AAP, 12 (63.2%) had grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events, the most common being thrombocytopenia (26.3%) and hypertension (21.1%). Five patients (26.3%) had adverse events leading to treatment discontinuation.
Conclusions: These results support the choice of niraparib 200 mg as the RP2D with AAP. The niraparib-AAP combination was tolerable in patients with mCRPC, with no new safety signals. An ongoing phase 3 study is further assessing this combination in patients with mCRPC.
Trial registration no: NCT02924766 (ClinicalTrials.gov).
Keywords: Androgen-signaling-targeted therapy; DRD genes; MCRPC; Niraparib; PARP inhibitors; Pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
Fred Saad has served as a consultant/advisor for Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Janssen, Merck, Myovant, and Sanofi and has received research funding from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck, Myovant, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Kim N. Chi has served as a consultant/advisor for Amgen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Constellation Pharmaceuticals, Daiichi Sankyo, ESSA, Janssen, Merck, Point Biopharma Inc., Roche, and Sanofi and has received honoraria from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Janssen, Merck, and Roche. Neal D. Shore reports personal fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Dendreon, Ferring, Janssen, Merck, Myovant, Pfizer, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Tolmar. Julie N. Graff reports institutional research funding from Astellas, Janssen, Merck, and Sanofi and has received travel grants from Clovis and Merck. Edwin M. Posadas reports honoraria from Pfizer; has served as an expert advisor for Breckenridge Pharmaceuticals; has received travel and accommodations expenses from TRACON Pharma; has served as a consultant for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Janssen, and Novartis; and has received institutional research support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera, IMV, Janssen, Merck, Peleton, and Pfizer. Jean-Baptiste Lattouf has served as a consultant/advisor for Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, and Sanofi and has conducted clinical research for Aragon Pharmaceutical, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck, Myovant, Pfizer, Progenics, and Tokai Pharmaceuticals. Byron M. Espina, Eugene Zhu, Alex Yu, Anasuya Hazra, Marc De Meulder, Rao N. V. S. Mamidi, Branislav Bradic, Peter Francis, and Vinny Hayreh are employees of Janssen Research & Development, LLC, and may hold stock and/or stock options. Arash Rezazadeh Kalebasty has served as a consultant/advisor/review panel member for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Genentech, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi; has received grant/institutional research support from Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bavarian Nordic, Bayer, BeyondSpring Pharma, BioClin Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Clovis Oncology, Eisai, Epizyme, Exelixis, Genentech, Immunomedics, Janssen, Macrogenics, Novartis, Pfizer, and Seattle Genetics; has participated in speakers’ bureau for Amgen, Astellas Medivation, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Seattle Genetics/Astellas; has received honorarium from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Exelixis, Novartis, and Pfizer; has received travel, accommodation, and expenses from Astellas Medivation, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Eisai, Exelixis, Genentech, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Prometheus; and reports stock and other ownership interest in ECOM Medical.
Figures
References
-
- Ryan CJ, Smith MR, Fizazi K, Saad F, Mulders PF, Sternberg CN, Miller K, Logothetis CJ, Shore ND, Small EJ, Carles J, Flaig TW, Taplin ME, Higano CS, de Souza P, de Bono JS, Griffin TW, De Porre P, Yu MK, Park YC, Li J, Kheoh T, Naini V, Molina A, Rathkopf DE, Investigators C-A-, Abiraterone acetate plus prednisone versus placebo plus prednisone in chemotherapy-naive men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (COU-AA-302): final overall survival analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(2):152–160. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71205-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beer TM, Armstrong AJ, Rathkopf DE, Loriot Y, Sternberg CN, Higano CS, Iversen P, Bhattacharya S, Carles J, Chowdhury S, Davis ID, de Bono JS, Evans CP, Fizazi K, Joshua AM, Kim CS, Kimura G, Mainwaring P, Mansbach H, Miller K, Noonberg SB, Perabo F, Phung D, Saad F, Scher HI, Taplin ME, Venner PM, Tombal B, Investigators P. Enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer before chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(5):424–433. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1405095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Bono JS, Logothetis CJ, Molina A, Fizazi K, North S, Chu L, Chi KN, Jones RJ, Goodman OB, Jr, Saad F, Staffurth JN, Mainwaring P, Harland S, Flaig TW, Hutson TE, Cheng T, Patterson H, Hainsworth JD, Ryan CJ, Sternberg CN, Ellard SL, Flechon A, Saleh M, Scholz M, Efstathiou E, Zivi A, Bianchini D, Loriot Y, Chieffo N, Kheoh T, Haqq CM, Scher HI, Investigators C-A- Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(21):1995–2005. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1014618. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ryan CJ, Smith MR, de Bono JS, Molina A, Logothetis CJ, de Souza P, Fizazi K, Mainwaring P, Piulats JM, Ng S, Carles J, Mulders PF, Basch E, Small EJ, Saad F, Schrijvers D, Van Poppel H, Mukherjee SD, Suttmann H, Gerritsen WR, Flaig TW, George DJ, Yu EY, Efstathiou E, Pantuck A, Winquist E, Higano CS, Taplin ME, Park Y, Kheoh T, Griffin T, Scher HI, Rathkopf DE, Investigators C-A- Abiraterone in metastatic prostate cancer without previous chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(2):138–148. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1209096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

