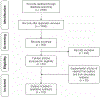
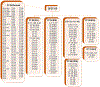
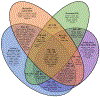
Fig. 3
Overlap between AS, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and psoriasis susceptibility genes. ACTA2, alpha actin 2, smooth muscle aortic; ADCY3, adenylate cyclase 3; ANKRD55, ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 55; ANTXR2, anthrax toxin receptor 2; ASAP2, ArfGAP with SH3 domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 2; ATG16L1, autophagy16-like 1; BACH2, BTB and CNC homology 2; BANK1, B cell scaffold protein with ankyrin repeats-1; BSN, bassoon mouse, homolog of (zinc finger 231); C17orf67, chromosome 17 open reading frame 67; CARD9, caspase recruitment domain family member 9; CCL21, C-C motif chemokine ligand 21; CD6, CD6 molecule; CD28, CD28 molecule; CD40, CD40 molecule; CD226, CD226 molecule; CDKAL1, CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 1 like 1; CLEC16A, C-type lectin domain containing 16A; CMC1, C-X9-C motif containing 1; CPEB4, cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 4; CREM, cAMP responsive element modulator; CXCR2, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2; DAP, death-associated protein; DENND1B, DENN domain containing 1B; DLEU1, deleted in lymphocyte leukemia 1; DNMT3A, DNA methyltransferase 3 alpha; DNMT3B, DNA methyltransferase 3 beta; EIF2S2P3, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 2 beta pseudogene 3; ERAP1, endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1; ERAP2, endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2; ERN1, endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 1; ETS1, ETS proto-oncogene 1, transcription factor; FAM118A, family with sequence similarity 118 member A; FAP, fibroblast activation protein alpha; FBXL19, F-box and leucine rich repeat protein 19; FCGR2A, Fc fragment of IgG receptor IIa; FGFR1OP, FGFR1 oncogene partner; FIBP, FGF1 intracellular binding protein; FNDC3A, fibronectin type III domain containing 3A; FOS-V, Finkel-Biskis-Jinkins murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog; FOSL2, FOS-related antigen 2; FUT2, fucosyltransferase 2; GAL3ST2, galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 2; GBAP1, glucosylceramidase beta pseudogene 1; GCKR, glucokinase regulator; GLYAT, glycine-N-acyltransferase; GNA12, G protein subunit alpha 12; GPR35, G protein-coupled receptor 35; HDAC7, histone deacetylase 7; HIPK1, homeodomain interacting protein kinase 1; HLA-A, human eukocyte antigen A; HLA-B, human leukocyte antigen B; HLA-C, human leukocyte antigen C; HLA-DP, human leukocyte antigen DP; HLA-DRA, human leukocyte antigen DR alpha; HLA-DRB1, human leukocyte antigen DR beta 1; HMGN2P18, high mobility group nucleosomal binding domain 2 pseudogene 18; HNF4A, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha; HSPA6, heat shock 70kd protein 6; ICOSLG, inducible T cell costimulator ligand; IFIH1, interferon-induced helicase C domain-containing protein 1; IFNG-AS1, interferon gamma; IFNGR2, interferon gamma receptor 2; IFNLR1, interferon lambda receptor 1; IL1R1, interleukin 1 receptor type 1; IL1R2, interleukin 1 receptor type 2; IL2RA, interleukin 2 receptor alpha; IL6R, interleukin 6 receptor; IL7R, Interleukin 7 receptor; IL10, interleukin 10; IL12B, interleukin 12B (IL12 p40 subunit); IL18R1, interleukin 18 receptor 1 (alpha chain); IL21, interleukin 21; IL23A, interleukin 23 alpha (IL12 p19 subunit); IL23R, interleukin 23 receptor; IL27, interleukin 27; INAVA, innate immunity activator; IRF1, interferon regulatory factor 1; IRF5, interferon regulatory factor 5; IRGM, immunity-related GTPase family, M; ITGAL, integrin alpha-L; ITLN1, intelectin 1; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; JAZF1, JAZF zinc finger 1; KEAP1, kelch like ECH associated protein 1; KIF21B, kinesin family member 21B; KSR1, kinase suppressor of ras 1; LCE3B, late cornified envelope 3B; LNPEP, leucyl-cystinyl aminopeptidase; LRRK2, leucine rich repeat kinase 2; LSM14A, LSM14A mRNA processing body assembly factor; LTBR, lymphotoxin B receptor; MST1, macrophage stimulating 1; MYRF, myelin regulatory factor; NDFIP1, neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally downregulated 4 family-interacting protein 1; NFATC1, nuclear factor of activated t cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1; NFIP1; Nedd4 Family Interacting Protein 1;NFKB1, nuclear factor kappa-b, subunit 1; NFKBIA, nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in b cells inhibitor, alpha; NKX2-3, NK2 homeobox 3; NOD2, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain protein 2; NOS2, nitric oxide synthase 2A; NOTCH1, NOTCH, Drosophila, homolog of, 1; NPEPPS, aminopeptidase, puromycin-sensitive; NR5A2, nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 2; NXPE1, neurexophilin and PC-esterase domain family member 1; OR5B21, olfactory receptor family 5 subfamily B member 21; OSMR, oncostatin M receptor; PARK7, Parkinsonism associated deglycase; PKIG, cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor gamma; PLAU, plasminogen activator, urokinase; PPP2R3C, protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit B double prime gamma; PPP5C, protein phosphatase 5 catalytic subunit; PRDM1, PR domain-containing protein 1; PRKCB, protein kinase C beta; PRKCQ, protein kinase C theta; PTGER4, prostaglandin E receptor 4, EP4 subtype; PTPN2, protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 2; PTPN22, protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 22; PUS10, pseudouridylate synthase 10; RAVER1, RAVER1, mouse, homolog of; RIC8B, RIC8, C. elegans, homolog of, B; RNF114, ring finger protein 114; RNF186, ring finger protein 186; RORC, RAR-related orphan receptor C; RPS6KB1, ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 70-Kd, 1; RUNX3, runt-related transcription factor 3; SBNO2, strawberry notch, Drosophila, homolog of, 2; SDF4, stromal cell derived factor 4; SETD1A, SET domain-containing protein 1A; SH2B3, SH2B adaptor protein 3; SKAP2, SRC kinase-associated phosphoprotein 2; SLC9A8, solute carrier family 9 (zinc transporter), member 8; SLC26A3, solute carrier family 26 (zinc transporter), member 26; SLC39A11, solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 11; SMAD3, mothers against decapentaplegic, Drosophila, homolog of, 3; SP140, nuclear body protein SP140; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; STK11, serine/threonine protein kinase 11; SULT1A2, sulfotransferase family 1A, cytosolic-phenol preferring member 2; TBKBP1, tank binding kinase binding protein 1; TBX21, T-box 21; TEX41, testis expressed 41; THADA, thyroid adenoma associated gene; TLR4, Toll receptor 4; TNFAIP3, tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3; TNFRSF1A, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1A; TNFRSF6B, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 6B; TNFRSF14, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 14; TNFSF8, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily, member 8; TNFSF15, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily, member 15; TNIP1, TNFAIP3-interacting protein 1; TNP2, transition protein 2; TSPAN14, tetraspanin 14; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2; UBAC2, UBA domain-containing protein 2; UBASH3, ubiquitin-associated and SH3 domain-containing protein A; UBE2L3, ubiquitin conjugating enzyme 2EL 3; UQCR10, ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex, 7.2 kd subunit; ZPBP2, zona pellucida-binding protein 2; ZC3H12C, zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 12C; ZMIZ1, Zinc finger MIZ-domain containing 1; ZNF365, zinc finger protein 365; ZNF831, melanoma, cutaneous malignant-susceptibility to 1. Not shown are genetic markers from noncoding regions: AC008697.1, Homo sapiens chromosome 5 clone CIT978SKB_70D3; AC020743.4, Homo sapiens chromosome 7 clone RP11-813 K3; AL031590.1, Homo sapiens chromosome 22, clone 232D4; AP001057.1, uncharacterized LOC107983952; CTD-2260A1, DNA marker; NPM1P17, nucleophosmin 1 pseudogene 17; RP1-66C13.4; RP11-24F11.2; RP11-129 J12.1; RP11-300 J18.1; RP11-1C1.5; RP11-84D1.2; and RP11-672A2.7