Hand Grip and Leg Muscle Strength in Hemodialysis Patients and Its Determinants
- PMID: 33754509
- PMCID: PMC7985287
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e76
Hand Grip and Leg Muscle Strength in Hemodialysis Patients and Its Determinants
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease is associated with chronic inflammation and progressive loss of peripheral muscle strength and the ability to exercise, and these changes are highly pronounced in patients receiving hemodialysis (HD). We evaluated hand grip strength (HGS) and leg muscle strength (LMS) in patients receiving HD and attempted to identify factors associated with muscle strength.
Methods: We screened HGS (opposite the fistula side) and LMS (both sides) in HD patients at a single center (n = 112) by using digital hand and leg dynamometers (T.K.K. 5401 and 5710e/5715, Takei Scientific Instruments Co. Ltd., Niigata, Japan).
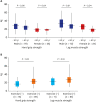
Results: The mean age of patients was 62.6 years, and 73.2% of the patients were male. Diabetes was the cause of kidney failure in 50% of the patients, and the median HD vintage was 34 months. A total of 77.7% of patients reported that they participated in regular home-based exercise, and 29.5% of patients regularly participated in hospital-based resistance exercise. HGS and LMS showed good correlation (r = 0.715, P < 0.001). HGS (25.1 vs. 17.0 kg) and LMS (30.1 vs. 20.4 kg) were greater in males (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively) than in females. Older patients (≥ 60 years) showed less LMS than younger patients in both males and females (P = 0.012 and P = 0.037, respectively), but HGS did not differ according to age. Patients performing regular home- or hospital-based exercise showed higher HGS than those who did not exercise (24.2 vs. 18.6 kg, P = 0.011), but LMS was not significantly different (29.3 vs. 23.6 kg, P = 0.185). Multiple linear regression analysis proved that male sex, younger age, and any type of exercise were factors associated with improved HGS and LMS. Groups of older age (≥ 60 years), male sex, and shorter duration of HD (< median) benefitted more from exercise.
Conclusion: Sex, age, and exercise were the most important determinants of muscle strength in HD patients. We need to encourage patients to engage in regular home or group exercise from the beginning of dialysis and introduce new feasible forms of exercise for HD patients.
Keywords: Hand Grip Strength; Hemodialysis; Leg Muscle Strength.
© 2021 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Fouque D, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple J, Cano N, Chauveau P, Cuppari L, et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008;73(4):391–398. - PubMed
-
- Hanna RM, Ghobry L, Wassef O, Rhee CM, Kalantar-Zadeh K. A practical approach to nutrition, protein-energy wasting, sarcopenia, and cachexia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2020;49(1-2):202–211. - PubMed
-
- Moon SJ, Kim TH, Yoon SY, Chung JH, Hwang HJ. Relationship between stage of chronic kidney disease and sarcopenia in Korean aged 40 years and older using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES IV-2, 3, and V-1, 2), 2008–2011. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0130740. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fahal IH. Uraemic sarcopenia: aetiology and implications. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29(9):1655–1665. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical