Genomic Analysis of Novel Poxvirus Brazilian Porcupinepox Virus, Brazil, 2019
- PMID: 33754985
- PMCID: PMC8007330
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2704.203818
Genomic Analysis of Novel Poxvirus Brazilian Porcupinepox Virus, Brazil, 2019
Abstract
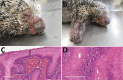
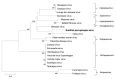
We obtained the complete sequence of a novel poxvirus, tentatively named Brazilian porcupinepox virus, from a wild porcupine (Coendou prehensilis) in Brazil that had skin and internal lesions characteristic of poxvirus infection. The impact of this lethal poxvirus on the survival of this species and its potential zoonotic importance remain to be investigated.
Keywords: Brazil; Brazilian porcupinepox virus; Chordopoxvirinae; Poxviridae; emerging infectious; novel poxvirus; viral disease; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

