Stability of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Nonsupplemented Saliva
- PMID: 33754989
- PMCID: PMC8007305
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2704.204199
Stability of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Nonsupplemented Saliva
Abstract
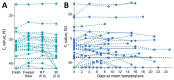
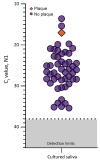
The expense of saliva collection devices designed to stabilize severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 RNA is prohibitive to mass testing. However, virus RNA in nonsupplemented saliva is stable for extended periods and at elevated temperatures. Simple plastic tubes for saliva collection will make large-scale testing and continued surveillance easier.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus disease; diagnostics; respiratory infections; saliva; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
Update of
-
Simply saliva: stability of SARS-CoV-2 detection negates the need for expensive collection devices.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 4:2020.08.03.20165233. doi: 10.1101/2020.08.03.20165233. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: Emerg Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;27(4):1146-1150. doi: 10.3201/eid2704.204199. PMID: 32793924 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hanson KE, Barker AP, Hillyard DR, Gilmore N, Barrett JW, Orlandi RR, et al. Self-collected anterior nasal and saliva specimens versus health care worker-collected nasopharyngeal swabs for the molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58:e01824–20. 10.1128/JCM.01824-20 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

