The Impact of Social Distancing for COVID-19 Upon Diagnosis of Kawasaki Disease
- PMID: 33755140
- PMCID: PMC8083704
- DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piab013
The Impact of Social Distancing for COVID-19 Upon Diagnosis of Kawasaki Disease
Abstract
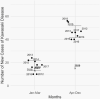
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mitigation policies have been associated with profound decreases in diagnoses of common childhood respiratory infections. A leading theory of etiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) is that it is triggered by presently unidentified ubiquitous respiratory agent. We document that mitigation policies instituted in mid-March 2020 were associated with strikingly fewer diagnoses of KD in April-December 2020 compared with the same period in the previous 8 years (P = .01), a >67% decline. This finding supports the hypothesis that KD is caused by a respiratory-transmitted agent.
Keywords: COVID-19; Kawasaki disease; mitigation; respiratory transmission; social distancing.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Hatoun J, Correa ET, Donahue SMA, Vernacchio L. Social distancing for COVID-19 and diagnoses of other infectious diseases in children. Pediatrics 2020; 146:e202006460. - PubMed
-
- McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, et al. . Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease. Circulation 2017; 135:E927–99. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

