The impact of the coronavirus disease and Tele-Heart Failure Clinic on cardiovascular mortality and heart failure hospitalization in ambulatory patients with heart failure
- PMID: 33755715
- PMCID: PMC7987182
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249043
The impact of the coronavirus disease and Tele-Heart Failure Clinic on cardiovascular mortality and heart failure hospitalization in ambulatory patients with heart failure
Abstract
Background: We sought to investigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the Tele-HF Clinic (Tele-HFC) program on cardiovascular death, heart failure (HF) rehospitalization, and heart transplantation rates in a cohort of ambulatory HF patients during and after the peak of the pandemic.
Methods: Using the HF clinic database, we compared data of patients with HF before, during, and after the peak of the pandemic (January 1 to March 17 [pre-COVID], March 17 to May 31 [peak-COVID], and June 1 to October 1 [post-COVID]). During peak-COVID, all patients were managed by Tele-HFC or hospitalization. After June 1, patients chose either a face-to-face clinic visit or a continuous tele-clinic visit.
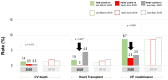
Results: Cardiovascular death and medical titration rates were similar in peak-COVID compared with all other periods. HF readmission rates were significantly lower in peak-COVID (8.7% vs. 2.5%, p<0.001) and slightly increased (3.5%) post-COVID. Heart transplant rates were substantially increased in post-COVID (4.5% vs. peak-COVID [0%], p = 0.002). After June 1, 38% of patients continued with the Tele-HFC program. Patients managed by the Tele-HFC program for <6 months were less likely to have HF with reduced ejection fraction (73% vs. 54%, p = 0.005) and stage-D HF (33% vs. 14%, p = 0.001), and more likely to achieve the target neurohormonal blockade dose (p<0.01), compared with the ≥6-month Tele-HFC group.
Conclusions: HF rehospitalization and transplant rates significantly declined during the pandemic in ambulatory care of HF. However, reduction in these rates did not affect subsequent 5-month hospitalization and cardiovascular mortality in the setting of Tele-HFC program and continuum of advanced HF therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr., Drazner MH, et al.. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:1810–52. 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829e8807 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

