Simvastatin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting TMEM16A Ca2+-activated chloride channel
- PMID: 33755783
- PMCID: PMC11801952
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-021-03575-w
Simvastatin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting TMEM16A Ca2+-activated chloride channel
Abstract
Purpose: Ca2+-activated chloride channel TMEM16A has been found to be overexpressed in many cancers including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Nevertheless, the role of TMEM16A in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) remains unclear. Although simvastatin is known to produce anti-tumor effect, the mechanisms by which simvastatin inhibits cancer remain unclear.
Methods: In this study, we explored the role of TMEM16A expression in human OSCC tissues using both TCGA dataset and immunohistochemistry. CCK-8 assay was applied to evaluate cell proliferation. Patch clamp technique was applied to record TMEM16A Cl- currents.
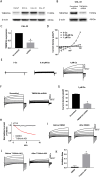
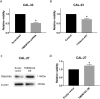
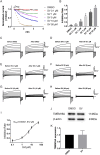
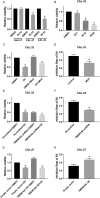
Results: We found that high TMEM16A expression is related with large tumor size, lymph node metastasis, and poor clinical outcome in patients with OSCC. In addition, TMEM16A overexpression could promote cell proliferation, and inhibition of TMEM16A channel activities could suppress cell proliferation in OSCC cells. Furthermore, simvastatin could suppress TMEM16A channel activities, and inhibited cell proliferation in OSCC cells via TMEM16A.
Conclusion: Our findings identify a novel anti-tumor mechanism of simvastatin by targeting TMEM16A. Simvastatin may represent an innovative strategy for treating OSCC with high TMEM16A expression.
Keywords: Ca2+-activated chloride channel; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Simvastatin; TMEM16A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics identification and validation of m6A/m1A/m5C/m7G/ac4 C-modified genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1055. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14216-7. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597017 Free PMC article.
-
Pathobiological role of cleft palate transmembrane protein 1 family proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Apr;145(4):851-859. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02843-0. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30635792 Free PMC article.
-
CSN6 promotes malignant progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by down-regulating TIMP-2.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 May;24(10):5419-5428. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202005_21326. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32495877
-
The diagnostic value of 11q13 amplification and protein expression in the detection of nodal metastasis from oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Virchows Arch. 2015 Apr;466(4):363-73. doi: 10.1007/s00428-015-1719-6. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Virchows Arch. 2015. PMID: 25663615 Free PMC article.
-
Management of clinically node-negative early-stage oral cancer: network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024 Mar;53(3):179-190. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2023.08.004. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 37661515 Review.
Cited by
-
The regulatory role and mechanism of energy metabolism and immune response in head and neck cancer.Genes Dis. 2025 Mar 19;12(6):101607. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101607. eCollection 2025 Nov. Genes Dis. 2025. PMID: 40821122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anoctamins and Calcium Signalling: An Obstacle to EGFR Targeted Therapy in Glioblastoma?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;14(23):5932. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235932. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and validation of a signature involving voltage-gated chloride ion channel genes for prediction of prostate cancer recurrence.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 30;13:1001634. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1001634. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36246902 Free PMC article.
-
Statins in Cancer Prevention and Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;15(15):3948. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153948. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion Channels as Potential Tools for the Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of HPV-Associated Cancers.Cells. 2023 May 12;12(10):1376. doi: 10.3390/cells12101376. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bellosta S, Paoletti R, Corsini A (2004) Safety of statins: focus on clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Circulation 109:50–57. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000131519.15067.1f - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. 10.3322/caac.21492 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

