mTORC1 promotes cell growth via m6A-dependent mRNA degradation
- PMID: 33756105
- PMCID: PMC8356906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.010
mTORC1 promotes cell growth via m6A-dependent mRNA degradation
Abstract
Dysregulated mTORC1 signaling alters a wide range of cellular processes, contributing to metabolic disorders and cancer. Defining the molecular details of downstream effectors is thus critical for uncovering selective therapeutic targets. We report that mTORC1 and its downstream kinase S6K enhance eIF4A/4B-mediated translation of Wilms' tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP), an adaptor for the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methyltransferase complex. This regulation is mediated by 5' UTR of WTAP mRNA that is targeted by eIF4A/4B. Single-nucleotide-resolution m6A mapping revealed that MAX dimerization protein 2 (MXD2) mRNA contains m6A, and increased m6A modification enhances its degradation. WTAP induces cMyc-MAX association by suppressing MXD2 expression, which promotes cMyc transcriptional activity and proliferation of mTORC1-activated cancer cells. These results elucidate a mechanism whereby mTORC1 stimulates oncogenic signaling via m6A RNA modification and illuminates the WTAP-MXD2-cMyc axis as a potential therapeutic target for mTORC1-driven cancers.
Keywords: MXD2; Protein translation; S6K1; WTAP; YTHDF readers; cMyc; eIF4A; m(6)A mRNA modification; mRNA stability; mTORC1.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.B. is an advisory board member for Molecular Cell. S.R.J. is scientific founder of, is advisor to, and owns equity in Gotham Therapeutics.
Figures
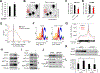
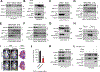
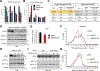
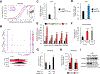

Comment in
-
More writing: mTORC1 promotes m6A mRNA methylation.Mol Cell. 2021 May 20;81(10):2057-2058. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.04.020. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34019785
References
-
- Barbieri I, and Kouzarides T. (2020). Role of RNA modifications in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 1–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD023669/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121266/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA062948/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DK113643/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA203702/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA120964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR057352/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM051405/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA221104/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS111631/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA186702/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

