Real-Life Experience of Monoclonal Antibody Treatments in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis
- PMID: 33756474
- PMCID: PMC8491492
- DOI: 10.1159/000514262
Real-Life Experience of Monoclonal Antibody Treatments in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis
Abstract
Introduction: Few studies assess biologicals such as, omalizumab, mepolizumab, benralizumab, and dupilumab in patients suffering from chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP). The reported success rate in these studies differ, and it remains uncertain if there are any biomarkers to predict successful therapy. Our aim was to analyze the therapeutic outcome in a real life setting and to identify predictive biomarkers for successful treatment.
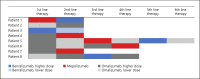
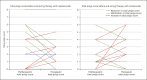
Methods: Data from patients with CRSwNP treated with a monoclonal antibody between November 2014 and January 2020 were analyzed retrospectively. Improvement in the polyp score and clinical symptoms like nasal obstruction, sense of smell, nasal discharge, and facial pain were evaluated. Other characteristics, including use of nasal or systemic steroids, comorbidities, previous history of sinus surgery, eosinophilia tissue, blood values (eosinophils, total immunoglobulin E, eosinophilic cationic protein, and interleukin 5), and allergic sensitization in serum were also investigated to identify possible predictive biomarkers.
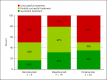
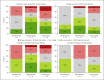
Results: Forty-eight treatments in 29 patients (m/f = 15/14) aged 27-70 years were reviewed. Treatments with mepolizumab showed the best success rates (78.9%), followed by omalizumab (50%) and benralizumab treatments (50%). However, a correlation between biomarkers and treatment success could not be found.
Discussion/conclusion: Treatment of CRSwNP with biologicals is a promising option for severe cases not responding to conventional therapy, including difficult-to-treat patients. Predictive biomarkers for a successful treatment could not be identified, but the reduction of eosinophilic cationic protein was linked with the response.
Keywords: Benralizumab; Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis; Mepolizumab; Monoclonal antibody; Omalizumab.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
M.B.S. acted as a consultant in a study on Dupilumab and received consulting fees by Biomedical Systems/Sanofi. P.S.G. has received speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Sanofi-Genzyme. No other author has reported any competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hastan D, Fokkens WJ, Bachert C, Newson RB, Bislimovska J, Bockelbrink A, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis in Europe–an underestimated disease. A GA(2)LEN study. Allergy. 2011;66((9)):1216–23. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, Hellings PW, Kern R, Reitsma S, et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology. 2020;58((Suppl S29)):1–464. - PubMed
-
- Gevaert P, Van Bruaene N, Cattaert T, Van Steen K, Van Zele T, Acke F, et al. Mepolizumab, a humanized anti-IL-5 mAb, as a treatment option for severe nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128((5)):989–95.e1–8. - PubMed
-
- Gevaert P, Calus L, Van Zele T, Blomme K, De Ruyck N, Bauters W, et al. Omalizumab is effective in allergic and nonallergic patients with nasal polyps and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131((1)):110–6.e1. - PubMed
-
- Bachert C, Mannent L, Naclerio RM, Mullol J, Ferguson BJ, Gevaert P, et al. Effect of subcutaneous dupilumab on nasal polyp burden in patients with chronic sinusitis and nasal polyposis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;315((5)):469–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

