Preclinical and clinical evidence of IGF-1 as a prognostic marker and acute intervention with ischemic stroke
- PMID: 33757314
- PMCID: PMC8504958
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X211000894
Preclinical and clinical evidence of IGF-1 as a prognostic marker and acute intervention with ischemic stroke
Abstract
Ischemic strokes are highly prevalent in the elderly population and are a leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. The risk of ischemic stroke increases in advanced age, corresponding with a noted decrease in circulating insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1). IGF-1 is a known neuroprotectant involved in embryonic development, neurogenesis, neurotransmission, cognition, and lifespan. Clinically, several studies have shown that reduced levels of IGF-1 correlate with increased mortality rate, poorer functional outcomes, and increased morbidities following an ischemic stroke. In animal models of ischemia, administering exogenous IGF-1 using various routes of administration (intranasal, intravenous, subcutaneous, or topical) at various time points prior to and following insult attenuates neurological damage and accompanying behavioral changes caused by ischemia. However, there are some contrasting findings in select clinical and preclinical studies. This review discusses the role of IGF-1 as a determinant factor of ischemic stroke outcomes, both within the clinical settings and preclinical animal models. Furthermore, the review provides insight on the role of IGF-1 in mechanisms and cellular processes that contribute to stroke damage.
Keywords: Somatomedin C; glia; ischemia; neurodegeneration; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
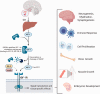


Similar articles
-
Exogenous insulin-like growth factor 1 attenuates acute ischemic stroke-induced spatial memory impairment via modulating inflammatory response and tau phosphorylation.Neuropeptides. 2020 Oct;83:102082. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2020.102082. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Neuropeptides. 2020. PMID: 32863068
-
Insulin-like growth factor I: a potential neuroprotective compound for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke?Stroke. 2009 Apr;40(4):e83-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.528356. Epub 2009 Feb 5. Stroke. 2009. PMID: 19197073 Review.
-
Neuronal and Astrocyte Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Signaling Differentially Modulates Ischemic Stroke Damage.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 2:2023.04.02.535245. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.02.535245. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37034764 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Spatial distribution of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 following hypoxic-ischemic injury.BMC Neurosci. 2013 Dec 21;14:158. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-14-158. BMC Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24359611 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 and cognitive health: Exploring cellular, preclinical, and clinical dimensions.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2025 Jan;76:101161. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2024.101161. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 39536910 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between insulin-like growth factor-1 and cerebral small vessel disease and its mechanisms: advances in the field.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jun 8;15:1190869. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1190869. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37358957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Differentially Modulates Glutamate-Induced Toxicity and Stress in Cells of the Neurogliovascular Unit.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Nov 23;13:751304. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.751304. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34887742 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the molecular mechanism of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1): a promising therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases associated with metabolic syndrome.Cell Biosci. 2023 Jan 23;13(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-00966-z. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36691085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uwhangchungsimwon Inhibits Oxygen Glucose Deprivation/Re-Oxygenation-Induced Cell Death through Neuronal VEGF and IGF-1 Receptor Signaling and Synaptic Remodeling in Cortical Neurons.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;11(7):1388. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071388. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883879 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy of Epidermal Growth Factor and Growth Hormone-Releasing Hexapeptide in acute ischemic stroke: a phase I/II non-blinded, randomized clinical trial.Front Neurol. 2024 Apr 4;15:1303402. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1303402. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38638315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al..; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019; 139: e56–e528. - PubMed
-
- Iso H, Maruyama K, Ikehara S, et al.. Cellular growth factors in relation to mortality from cardiovascular disease in middle-aged Japanese: the JACC study. Atherosclerosis 2012; 224: 154–160. - PubMed
-
- Guan J, Miller OT, Waugh KM, et al.. Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves somatosensory function and reduces the extent of cortical infarction and ongoing neuronal loss after hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Neuroscience 2001; 105: 299–306. - PubMed
-
- Grant MB, Wargovich TJ, Ellis EA, et al.. Expression of IGF-I, IGF-I receptor and IGF binding proteins-1, -2, -3, -4 and -5 in human atherectomy specimens. Regul Pept 1996; 67: 137–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

