Evaluation of cerebral dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease using neuropsychometric and neurophysiological tests
- PMID: 33757399
- PMCID: PMC7993379
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1901740
Evaluation of cerebral dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease using neuropsychometric and neurophysiological tests
Abstract
Background: Uremic encephalopathy is defined as cerebral dysfunction due to toxin accumulation in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). This condition is characterized by subtle to florid symptoms, and its clinical course is always progressive when untreated but partially reversible with renal replacement therapy. While no test exists to measure subclinical uremic encephalopathy, two tests have been validated to measure minimal hepatic encephalopathy: the critical flicker frequency (CFF) test and the psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES).
Objective: To use CFF and PHES to measure the prevalence of cerebral dysfunction in individuals with CKD.
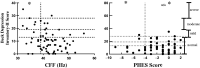
Methods: This cross-sectional study included a total of 69 patients with stage-5 CKD. Cutoff points for minimal encephalopathy were established using existing clinical guidelines: ≤39 Hz for CFF and < -4 for PHES. All participants were also screened for cognitive function and depression.
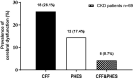
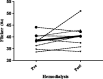
Results: Eighteen cases (26.1%) of cerebral dysfunction linked to uremic encephalopathy were detected with CFF, while twelve (17.4%) were detected by PHES; only six cases (8.7%) were diagnosed by both methods. Half of the cases (50%) had diabetes, and 61% were on hemodialysis. Cognitive function scores did not differ significantly between those receiving dialysis, hemodialysis, or no renal replacement therapy.
Conclusions: It is essential to identify cerebral dysfunction when uremic encephalopathy is in early subclinical stages to reduce preventable events as traffic and work accidents.
Keywords: Critical flicker frequency; cerebral dysfunction; chronic kidney failure; uremia; uremic encephalopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Levin A, Tonelli M, Bonventre J, et al. . Global kidney health 2017 and beyond: a roadmap for closing gaps in care, research, and policy. Lancet. 2017;390:1830–1888. - PubMed
-
- Olano CG, Akram SM, Bhatt H.. Uremic encephalopathy. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021. - PubMed
-
- Vanholder R, De Smet R, Glorieux G, et al. , For the European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox) . Review on uremic toxins: classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1934–1943. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
