Random forest model to identify factors associated with anabolic-androgenic steroid use
- PMID: 33757585
- PMCID: PMC7988984
- DOI: 10.1186/s13102-021-00257-5
Random forest model to identify factors associated with anabolic-androgenic steroid use
Abstract
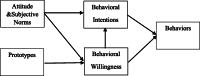
Background: One of the types of doping that is commonly used by bodybuilders, is androgenic-anabolic steroids (AAS). The use of AAS besides violating sporting ethics would have serious consequences on physical and mental health statuses. This study aimed to determine the most important factors of using AAS among bodybuilders by prototype willingness model (PWM).
Methods: In this analytical cross-sectional study, 280 male bodybuilders were selected from the bodybuilding clubs in Hamadan city using multistage sampling in 2016. A self-administered questionnaire consisting of demographic information and constructs of the PWM was then used to collect data and random forest model was also applied to analyze the collected data.
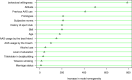
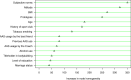
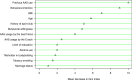
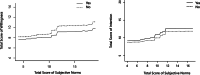
Results: Behavioral willingness, attitude, and previous AAS use were found as the most important factors in determining the behavioral intention. Moreover, subjective norms, attitude, BMI, and prototypes were the factors with the greatest effect on predicting behavioral willingness of AAS use. As well, behavioral intention was observed to be more important than behavioral willingness for predicting of AAS use.
Discussion: The obtained results show that the reasoned action path has a greater impact to predict AAS use among bodybuilders compared to social reaction path.
Keywords: Androgenic-anabolic steroids; Prototype willingness model; Random forest.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest in the undertaking of this research.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

