Blastomycosis Surveillance in 5 States, United States, 1987-2018
- PMID: 33757624
- PMCID: PMC8007286
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2704.204078
Blastomycosis Surveillance in 5 States, United States, 1987-2018
Abstract
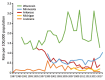
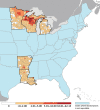
Blastomycosis is caused by inhalation of Blastomyces spp. fungi. Limited data are available on the incidence and geographic range of blastomycosis in the United States. To better characterize its epidemiologic features, we analyzed combined surveillance data from the 5 states in which blastomycosis is reportable: Arkansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin. Surveillance identified 4,441 cases during 1987–2018, a mean of 192 cases per year. The mean annual incidence was <1 case/100,000 population in most areas but >20 cases/100,000 population in some northern counties of Wisconsin. Median patient age was 46 years, 2,892 (65%) patients were male, 1,662 (57%) were hospitalized, and 278 (8%) died. The median time from symptom onset to diagnosis was 33 days. The severity of illness and diagnostic delays suggest that surveillance underestimates the true number of cases. More in-depth surveillance in additional states could elucidate blastomycosis incidence and inform efforts to increase awareness.
Keywords: Arkansas; Blastomycosis; Louisiana; Michigan; Minnesota; United States; Wisconsin; epidemiology; fungi; pneumonia; respiratory diseases; surveillance.
Figures
References
-
- Chapman SW, Dismukes WE, Proia LA, Bradsher RW, Pappas PG, Threlkeld MG, et al. ; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of blastomycosis: 2008 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:1801–12. 10.1086/588300 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

