Epidemiology of end-stage kidney disease
- PMID: 33757639
- PMCID: PMC8177747
- DOI: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2021.02.010
Epidemiology of end-stage kidney disease
Abstract
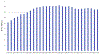
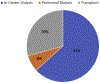
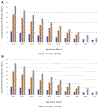
End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) is a common and morbid disease that affects patients' quality and length of life, representing a large portion of health care expenditure in the United States. These patients commonly have associated diabetes and cardiovascular disease, with high rates of cardiovascular-related death. Management of ESKD requires renal replacement therapy via dialysis or transplantation. While transplantation provides the greatest improvement in survival and quality of life, the vast majority of patients are treated initially with hemodialysis. However, outcomes differ significantly among patient populations. Barriers in access to care have particularly affected at-risk populations, such as Black and Hispanic patients. These patients receive less pre-ESKD nephrology care, are less likely to initiate dialysis with a fistula, and wait longer for transplants-even in pediatric populations. Priorities for ESKD care moving into the future include increasing access to nephrology care in underprivileged populations, providing patient-centered care based on each patient's "life plan," and focusing on team-based approaches to ESKD care. This review explores ESKD from the perspective of epidemiology, costs, vascular access, patient-reported outcomes, racial disparities, and the impact of the COVID-19 crisis.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- The Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) 2012 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Available at: https://kdigo.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/KDIGO_2012_CKD_GL.pdf. Accessed December 15, 2020.
-
- US Renal Data System. CKD in the general population. In: 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Volume 1, Chapter 1. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2020.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Age-adjusted prevalence of CKD stages 1–4 by gender 1999–2012. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Surveillance Project. Available at: https://nccd.cdc.gov. Accessed December 15, 2020.
-
- US Renal Data System. End stage renal disease: incidence, prevalence, patient characteristics, and treatment modalities. In: 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Volume 2, Chapter 1. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

