The Novel PII-Interacting Protein PirA Controls Flux into the Cyanobacterial Ornithine-Ammonia Cycle
- PMID: 33758091
- PMCID: PMC8092223
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00229-21
The Novel PII-Interacting Protein PirA Controls Flux into the Cyanobacterial Ornithine-Ammonia Cycle
Abstract
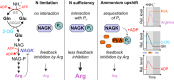
Among prokaryotes, cyanobacteria have an exclusive position as they perform oxygenic photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria substantially differ from other bacteria in further aspects, e.g., they evolved a plethora of unique regulatory mechanisms to control primary metabolism. This is exemplified by the regulation of glutamine synthetase (GS) via small proteins termed inactivating factors (IFs). Here, we reveal another small protein, encoded by the ssr0692 gene in the model strain Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, that regulates flux into the ornithine-ammonia cycle (OAC), the key hub of cyanobacterial nitrogen stockpiling and remobilization. This regulation is achieved by the interaction with the central carbon/nitrogen control protein PII, which commonly controls entry into the OAC by activating the key enzyme of arginine synthesis, N-acetyl-l-glutamate kinase (NAGK). In particular, the Ssr0692 protein competes with NAGK for PII binding and thereby prevents NAGK activation, which in turn lowers arginine synthesis. Accordingly, we termed it
Keywords: PII protein; cyanobacteria; nitrogen metabolism; small inhibitory proteins.
Copyright © 2021 Bolay et al.
Figures


Comment in
-
Studies on the Regulation of Arginine Metabolism in Cyanobacteria Should Include Mixotrophic Conditions.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0143321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01433-21. Epub 2021 Jun 22. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34154397 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Herrero A, Flores E, Imperial J. 2019. Nitrogen assimilation in bacteria, p 280–300. In Schmidt TM (ed), Encyclopedia of microbiology, 4th ed. Academic Press, Oxford, United Kingdom.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

