Comparative evaluation of metformin and liraglutide cardioprotective effect in rats with impaired glucose tolerance
- PMID: 33758265
- PMCID: PMC7987997
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86132-2
Comparative evaluation of metformin and liraglutide cardioprotective effect in rats with impaired glucose tolerance
Abstract
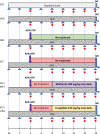
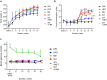
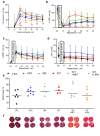
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) increases cardiovascular risk and can enlarge myocardial infarction (MI) incidence and severity. There is lack of information about cardioprotective potential of glucose-lowering drugs in IGT. We aimed to evaluate the sustainability of myocardium to ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic and IGT rats and to study cardioprotective action of metformin and liraglutide. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and IGT were modelled in Wistar rats by high-fat diet and streptozotocin + nicotinamide. 4 weeks after rats were divided into 4 groups: DM (without treatment) (n = 4), IGT (without treatment) (n = 4), IGT + MET (metformin 200 mg/kg per os once daily 8 weeks) (n = 4), IGT + LIRA (liraglutide 0.06 mg/kg s.c. once daily for 8 weeks) (n = 4). Control (n = 6) and high-fat diet (n = 8) groups were made for comparison. After 8 weeks ischemia-reperfusion injury in isolated hearts was performed. Hemodynamic parameters were evaluated and MI size was measured by staining of myocardium slices in triphenyltetrazolium chloride solution. Blood glucose level was measured during the study. Both IGT and DM led to similar worsening of hemodynamic parameters during ischemia-reperfusion period, in comparison with control group. MI size in IGT (56.76 (51.58; 69.07) %) and DM (57.26 (45.51; 70.08) %) groups was significantly larger than that in control group (42.98 (33.26; 61.84) %) and did not differ between each other. MI size in high-fat diet group (56.98 (47.11; 62.83) %) was as large as in IGT and DM groups (p > 0.05). MI size in IGT + MET (42.11 (38.08; 71.96) %) and IGT + LIRA (42.50 (31.37; 60.40) %) was smaller than in both DM and IGT groups (p < 0.05 for multiple comparison). Myocardium damage size did not differ in IGT + MET and IGT + LIRA groups (p > 0.05). Only LIRA, but not MET administration to IGT rats led to ischemic contracture reduction. Glycemic control was similarly satisfactory in IGT, IGT + MET, IGT + LIRA groups. Thus, IGT and DM have similarly pronounced negative influence on hemodynamics and MI size in rat transient global ischemia ex vivo. Obesity development also has negative impact on the MI size. Both MET and LIRA have infarct-limiting effect independent on their influence on glucose level. LIRA, but not MET, diminishes ischemic contracture in IGT rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/world/. Accessed 19 November 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

