Metabolic Messengers: FGF21
- PMID: 33758421
- PMCID: PMC8620721
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-021-00354-2
Metabolic Messengers: FGF21
Abstract
As a non-canonical fibroblast growth factor, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) functions as an endocrine hormone that signals to distinct targets throughout the body. Interest in therapeutic applications for FGF21 was initially sparked by its ability to correct metabolic dysfunction and decrease body weight associated with diabetes and obesity. More recently, new functions for FGF21 signalling have emerged, thus indicating that FGF21 is a dynamic molecule capable of regulating macronutrient preference and energy balance. Here, we highlight the major physiological and pharmacological effects of FGF21 related to nutrient and energy homeostasis and summarize current knowledge regarding FGF21’s pharmacodynamic properties. In addition, we provide new perspectives and highlight critical unanswered questions surrounding this unique metabolic messenger.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

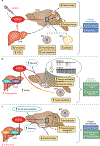
References
-
- Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M & Itoh N Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1492, 203–206 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

