Effectiveness of Pregabalin Treatment for Neuropathic Pain in Patients with Spine Diseases: A Pooled Analysis of Two Multicenter Observational Studies in Japan
- PMID: 33758538
- PMCID: PMC7981152
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S293556
Effectiveness of Pregabalin Treatment for Neuropathic Pain in Patients with Spine Diseases: A Pooled Analysis of Two Multicenter Observational Studies in Japan
Abstract
Purpose: Neuropathic pain (NeP) is common among patients with chronic pain associated with spine diseases. Practical effectiveness of pregabalin, one of the first-line treatments for NeP, has not been evaluated in an entire population of patients with spine diseases, including various pathophysiological conditions. This pooled analysis aimed to evaluate the therapeutic value of pregabalin for chronic pain with NeP component in patients with spine diseases in routine primary care settings.
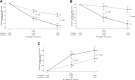
Patients and methods: We pooled data from two 8-week prospective observational cohort studies for patients with chronic low back pain with accompanying lower limb pain (NeP component), and patients with chronic cervical pain and accompanying upper limb radiating pain (NeP component) in routine primary care settings in Japan. For both studies, patients were treated for 8 weeks with pregabalin (alone/with other analgesics) or usual care with conventional analgesics (eg, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Changes in pain numerical rating scale (NRS), Pain-Related Sleep Interference Scale (PRSIS), and EuroQol 5-dimension 5-level (EQ-5D-5L) scores from baseline to week 8 were summarized and compared between the pregabalin and usual care groups, and also for subgroups of primary diagnosis. Safety was evaluated by adverse events (AEs) in the pregabalin group.
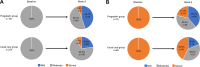
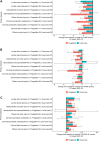
Results: The pooled dataset comprised 700 patients (pregabalin group: 302; usual care group: 398). All patient-reported outcomes (PRO) scores significantly improved from baseline to week 8 in the pregabalin than in the usual care group (NRS: P<0.0001; PRSIS: P<0.0001, and EQ-5D-5L: P=0.0006). Overall, all three PRO measures showed greater improvement in the pregabalin than in the usual care group, irrespective of the primary diagnosis. AEs were reported in 36.1% of the pregabalin group.
Conclusion: This analysis suggested multi-faceted effectiveness of treatment with pregabalin from the patient's perspectives under a "real-world" practice in all patients with chronic NeP from various spine diseases.
Keywords: chronic pain; neuropathic pain; pooled analysis; pregabalin; spine diseases.
© 2021 Taguchi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Shogo Nakano and Kazutaka Nozawa were employees of Pfizer Japan, Inc. at the time of study conduct and manuscript development. Toshihiko Taguchi was not financially compensated for their collaboration in this project or for the development of this manuscript, although Toshihiko Taguchi has received honorarium from Pfizer Japan Inc. outside of this work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest relevant to this work.
Figures
References
-
- International Association for the Study of Pain [homepage on the Internet]. Washington, D.C.: IASP Terminology; 2017. Available from: https://www.iasp-pain.org/terminology?navItemNumber=576#Neuropathicpain. Accessed May26, 2020.
-
- Ogawa S, Komatsu M, Ohno S, Yamane H, Hayakawa K. Pregabalin (Lyrica) Shiyou seiseki chousa: chukan kaiseki houkokusho [Interim report of drug use investigations of pregabalin (Lyrica)]. Prog Med. 2013;33(10):2159–2171.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

