RUNX2 as a promising therapeutic target for malignant tumors
- PMID: 33758548
- PMCID: PMC7981165
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S302173
RUNX2 as a promising therapeutic target for malignant tumors
Abstract
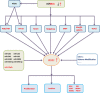
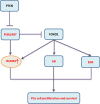
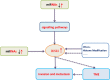
The transcription factor runt-related protein 2 (RUNX2) has an important impact on the transformation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts. Further studies have shown that RUNX2 plays a key role in the invasion and metastasis of cancers. RUNX2 is a "key" molecule in the regulatory network comprised of multiple signaling pathways upstream and its target downstream molecules. Due to the complex regulatory mechanisms of RUNX2, the specific mechanism underlying the occurrence, development and prognosis of malignant tumors has not been fully understood. Currently, RUNX2 as a promising therapeutic target for cancers has become a research hotspot. Herein, we reviewed the current literature on the modulatory functions and mechanisms of RUNX2 in the development of malignant tumors, aiming to explore its potential clinical application in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of tumors.
Keywords: RUNX2; malignant tumor;; research progress.
© 2021 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work and that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

