This is a preprint.
SARS-CoV-2 evolution in animals suggests mechanisms for rapid variant selection
- PMID: 33758844
- PMCID: PMC7987003
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.03.05.434135
SARS-CoV-2 evolution in animals suggests mechanisms for rapid variant selection
Update in
-
SARS-CoV-2 evolution in animals suggests mechanisms for rapid variant selection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov 2;118(44):e2105253118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2105253118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34716263 Free PMC article.
Abstract
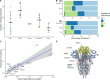
SARS-CoV-2 spillback from humans into domestic and wild animals has been well-documented. We compared variants of cell culture-expanded SARS-CoV-2 inoculum and virus recovered from four species following experimental exposure. Five nonsynonymous changes in nsp12, S, N and M genes were near fixation in the inoculum, but reverted to wild-type sequences in RNA recovered from dogs, cats and hamsters within 1-3 days post-exposure. Fourteen emergent variants were detected in viruses recovered from animals, including substitutions at spike positions H69, N501, and D614, which also vary in human lineages of concern. The rapidity of in vitro and in vivo SARS-CoV-2 selection reveals residues with functional significance during host-switching, illustrating the potential for spillback reservoir hosts to accelerate evolution, and demonstrating plasticity of viral adaptation in animal models.
One-sentence summary: SARS-CoV-2 variants rapidly arise in non-human hosts, revealing viral evolution and potential risk for human reinfection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


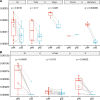
References
-
- Zhou P., lou Yang X., Wang X. G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H. R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C. L., Chen H. D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., di Jiang R., Liu M. Q., Chen Y., Shen X. R., Wang X., Zheng X. S., Zhao K., Chen Q. J., Deng F., Liu L. L., Yan B., Zhan F. X., Wang Y. Y., Xiao G. F., Shi Z. L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lam T. T. Y., Jia N., Zhang Y. W., Shum M. H. H., Jiang J. F., Zhu H. C., Tong Y. G., Shi Y. X., Ni X. B., Liao Y. S., Li W. J., Jiang B. G., Wei W., Yuan T. T., Zheng K., Cui X. M., Li J., Pei G. Q., Qiang X., Cheung W. Y. M., Li L. F., Sun F. F., Qin S., Huang J. C., Leung G. M., Holmes E. C., Hu Y. L., Guan Y., Cao W. C., Identifying SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature 583, 282–285 (2020). doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2169-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
