This is a preprint.
Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 within the household is associated with greater symptom severity and stronger antibody responses in a community-based sample of seropositive adults
- PMID: 33758903
- PMCID: PMC7987062
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.03.11.21253421
Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 within the household is associated with greater symptom severity and stronger antibody responses in a community-based sample of seropositive adults
Update in
-
Cohabitation With a Known Coronavirus Disease 2019 Case Is Associated With Greater Antibody Concentration and Symptom Severity in a Community-Based Sample of Seropositive Adults.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 24;8(7):ofab244. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofab244. eCollection 2021 Jul. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34316503 Free PMC article.
Abstract
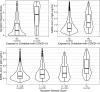
Magnitude of SARS-CoV-2 virus exposure may contribute to symptom severity. In a sample of seropositive adults (n=1101), we found that individuals who lived with a known COVID-19 case exhibited greater symptom severity and IgG concentrations compared to individuals who were seropositive but did not live with a known case (P<0.0001).
Figures
References
-
- Brodin P. Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity. Nat Med. 2021;27(1):28–33. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
