microRNA-mediated translation repression through GYF-1 and IFE-4 in C. elegans development
- PMID: 33758928
- PMCID: PMC8136787
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab162
microRNA-mediated translation repression through GYF-1 and IFE-4 in C. elegans development
Abstract
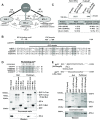
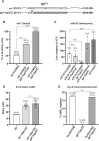
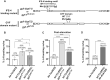
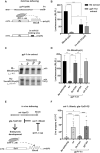
microRNA (miRNA)-mediated gene silencing is enacted through the recruitment of effector proteins that direct translational repression or degradation of mRNA targets, but the relative importance of their activities for animal development remains unknown. Our concerted proteomic surveys identified the uncharacterized GYF-domain encoding protein GYF-1 and its direct interaction with IFE-4, the ortholog of the mammalian translation repressor 4EHP, as key miRNA effector proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans. Recruitment of GYF-1 protein to mRNA reporters in vitro or in vivo leads to potent translation repression without affecting the poly(A) tail or impinging on mRNA stability. Loss of gyf-1 is synthetic lethal with hypomorphic alleles of embryonic miR-35-42 and larval (L4) let-7 miRNAs, which is phenocopied through engineered mutations in gyf-1 that abolish interaction with IFE-4. GYF-1/4EHP function is cascade-specific, as loss of gyf-1 had no noticeable impact on the functions of other miRNAs, including lin-4 and lsy-6. Overall, our findings reveal the first direct effector of miRNA-mediated translational repression in C. elegans and its physiological importance for the function of several, but likely not all miRNAs.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Ameres S.L., Zamore P.D.. Diversifying microRNA sequence and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013; 14:475. - PubMed
-
- Jonas S., Izaurralde E.. Towards a molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015; 16:421. - PubMed
-
- Iwakawa H.-o., Tomari Y.. The functions of MicroRNAs: mRNA decay and translational repression. Trends Cell Biol. 2015; 25:651–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

