Recombinant Soluble Corin Improves Cardiac Function in Mouse Models of Heart Failure
- PMID: 33759549
- PMCID: PMC8174325
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019961
Recombinant Soluble Corin Improves Cardiac Function in Mouse Models of Heart Failure
Abstract
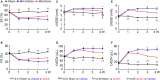
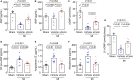
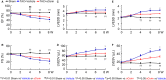
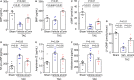
Background Corin is a transmembrane protease that activates ANP and BNP (atrial and B-type natriuretic peptides). Impaired corin expression and function are associated with heart failure. In this study, we characterized a soluble form of corin (sCorin) and examined its effects on cardiac morphology and function in mouse heart failure models. Methods and Results sCorin, consisting of the full-length extracellular fragment of human corin with an engineered activation site, was expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells, purified from the conditioned medium with affinity chromatography, and characterized in pro-ANP processing assays in vitro and pharmacokinetic studies in mice. Effects of sCorin on mouse models of heart failure induced by left coronary artery ligation and transverse aortic constriction were assessed by ELISA analysis of plasma markers, histologic examination, and echocardiography. We showed that purified and activated sCorin converted pro-ANP to ANP that stimulated cGMP production in cultured cells. In mice, intravenously and intraperitoneally administered sCorin had plasma half-lives of 3.5±0.1 and 8.3±0.3 hour, respectively. In the mouse heart failure models, intraperitoneal injection of sCorin increased plasma ANP, BNP, and cGMP levels; lowered plasma levels of NT-proANP (N-terminal-pro-ANP), angiotensin II, and aldosterone; reduced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis; and improved cardiac function. Conclusions We show that sCorin treatment enhanced natriuretic peptide processing and activity, suppressed the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and improved cardiac morphology and function in mice with failing hearts.
Keywords: cardiac function; cardiac hypertrophy; corin; heart failure; mouse models.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Wu is an inventor on several corin‐related patents that are owned by Bayer Healthcare. Dr Wu does not own Bayer stock and has not and will not receive any royalties from those patents. The remaining authors have no disclosures to report.
Figures



References
-
- Chen W, Spitzl A, Mathes D, Nikolaev VO, Werner F, Weirather J, Špiranec K, Röck K, Fischer JW, Kämmerer U, et al. Endothelial actions of ANP enhance myocardial inflammatory infiltration in the early phase after acute infarction. Circ Res. 2016;119:237–248. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307196. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holtwick R, van Eickels M, Skryabin BV, Baba HA, Bubikat A, Begrow F, Schneider MD, Garbers DL, Kuhn M. Pressure‐independent cardiac hypertrophy in mice with cardiomyocyte‐restricted inactivation of the atrial natriuretic peptide receptor guanylyl cyclase‐A. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:1399–1407. DOI: 10.1172/JCI17061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

