The ABCs of the atypical Fam20 secretory pathway kinases
- PMID: 33759783
- PMCID: PMC7948968
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100267
The ABCs of the atypical Fam20 secretory pathway kinases
Abstract
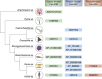
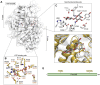
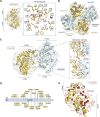
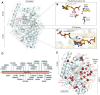
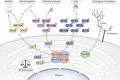
The study of extracellular phosphorylation was initiated in late 19th century when the secreted milk protein, casein, and egg-yolk protein, phosvitin, were shown to be phosphorylated. However, it took more than a century to identify Fam20C, which phosphorylates both casein and phosvitin under physiological conditions. This kinase, along with its family members Fam20A and Fam20B, defined a new family with altered amino acid sequences highly atypical from the canonical 540 kinases comprising the kinome. Fam20B is a glycan kinase that phosphorylates xylose residues and triggers peptidoglycan biosynthesis, a role conserved from sponges to human. The protein kinase, Fam20C, conserved from nematodes to humans, phosphorylates well over 100 substrates in the secretory pathway with overall functions postulated to encompass endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis, nutrition, cardiac function, coagulation, and biomineralization. The preferred phosphorylation motif of Fam20C is SxE/pS, and structural studies revealed that related member Fam20A allosterically activates Fam20C by forming a heterodimeric/tetrameric complex. Fam20A, a pseudokinase, is observed only in vertebrates. Loss-of-function genetic alterations in the Fam20 family lead to human diseases such as amelogenesis imperfecta, nephrocalcinosis, lethal and nonlethal forms of Raine syndrome with major skeletal defects, and altered phosphate homeostasis. Together, these three members of the Fam20 family modulate a diverse network of secretory pathway components playing crucial roles in health and disease. The overarching theme of this review is to highlight the progress that has been made in the emerging field of extracellular phosphorylation and the key roles secretory pathway kinases play in an ever-expanding number of cellular processes.
Keywords: Golgi; biomineralization; endoplasmic reticulum (ER); enzyme mutation; enzyme structure; extracellular matrix; phosphorylation; secretion; signal transduction.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Hammarsten O. Zur Frage ob das Caseïn ein einheitlicher Stoff sei. Z. Physiol. Chem. 1883;7:227–273.
-
- Leven P.A., Alsberg C. Zur chemie der paranucleinsaure. Hopper-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem. 1900;31:543–555.
-
- Meggio F., Boulton A.P., Marchiori F., Borin G., Lennon D.P., Calderan A., Pinna L.A. Substrate-specificity determinants for a membrane-bound casein kinase of lactating mammary gland. A study with synthetic peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988;177:281–284. - PubMed
-
- Byrne B.M., van het Schip A.D., van de Klundert J.A., Arnberg A.C., Gruber M., Ab G. Amino acid sequence of phosvitin derived from the nucleotide sequence of part of the chicken vitellogenin gene. Biochemistry. 1984;23:4275–4279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

