MicroRNA-124 facilitates lens epithelial cell apoptosis by inhibiting SPRY2 and MMP-2
- PMID: 33760112
- PMCID: PMC7986009
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12020
MicroRNA-124 facilitates lens epithelial cell apoptosis by inhibiting SPRY2 and MMP-2
Abstract
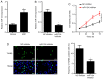
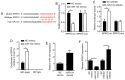
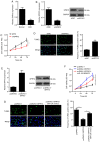
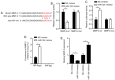
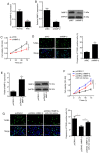
Age-related cataract (ARC) is the primary cause of blindness worldwide. Abnormal expression of microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs) has been reported to be associated with multiple diseases, including ARC. However, the potential role of miR-124 in ARC remains unclear. The present study used the human lens epithelial cell line, SRA01/04, to investigate the potential role of miR-124 in ARC. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR analysis was performed to detect the expression levels of miR-124, protein sprouty homolog 2 (SPRY2) and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) in ARC tissues, while western blotting was performed to detect the protein levels of SPRY2 and MMP-2. Cell viability and apoptosis of SRA01/04 cells were assessed via Cell Counting Kit-8 and TUNEL assays, respectively. The interaction between miR-124 and SPRY2 or MMP-2 was confirmed via the dual-luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation assays. The results of the present study demonstrated that miR-124 expression was significantly upregulated in ARC tissues, and knockdown of miR-124 increased SRA01/04 cell viability and suppressed apoptosis. In addition, SPRY2 and MMP-2 expression was decreased in ARC tissues, and were demonstrated to directly bind to miR-124. Overexpression of SPRY2 or MMP-2 increased SRA01/04 cell viability and repressed apoptosis, the effects of which were reversed following overexpression of miR-124. Taken together, these results suggested that miR-124 facilitates lens epithelial cell apoptosis by modulating SPRY2 or MMP-2 expression, providing a novel treatment approach for ARC.
Keywords: microRNA-124; protein sprouty homolog 2; matrix metalloproteinase-2; lens epithelial cells; age-related cataract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nangia V, Jonas JB, George R, Lingam V, Ellwein L, Cicinelli MV, Das A, Flaxman SR, Keeffe JE, Kempen JH, et al. Vision Loss Expert Group of the Global Burden of Disease Study Prevalence and causes of blindness and vision impairment: Magnitude, temporal trends and projections in South and Central Asia. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019;103:871–877. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-312292. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

