miR‑302c‑3p and miR‑520a‑3p suppress the proliferation of cervical carcinoma cells by targeting CXCL8
- PMID: 33760117
- PMCID: PMC7974325
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11961
miR‑302c‑3p and miR‑520a‑3p suppress the proliferation of cervical carcinoma cells by targeting CXCL8
Abstract
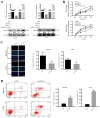
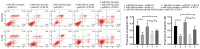
The aim of the present study was to identify the differentially expressed microRNAs (miRs) in cervical carcinoma (CC) tissues and cells and to explore the function of miR‑302c‑3p and miR‑520a‑3p in the proliferation of CC cells. Potential dysregulated miRNAs in CC tissues and tumour‑adjacent tissues were detected. Reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR (RT‑qPCR) was performed to determine the expression of miR‑302c‑3p, miR‑520a‑3p and CXCL8 in CC tissues and cell lines. The target genes of the miRNAs were predicted using miRTarBase and verified by luciferase reporter assays. RT‑qPCR and western blotting were performed to measure the expression of C‑X‑C motif ligand (CXCL)8 after transfection. The effect on proliferation was verified by Cell Counting Kit assay and ethynyl‑2‑deoxyuridine staining. Flow cytometry was utilised to assess the effect on apoptosis. In the present study, miR‑302c‑3p and miR‑520a‑3p were markedly downregulated in CC cell lines compared to the normal cervical cell line H8. Functionally, overexpression of miR‑302c‑3p and/or miR‑520a‑3p inhibited proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of CC cell lines in vitro, while the knockdown of miR‑302c‑3p and/or miR‑520a‑3p had the opposite effect. Furthermore, miR‑302c‑3p and miR‑520a‑3p could both bind to CXCL8. Inhibition of CXCL8 in combination with miR‑302c‑3p and/or miR‑520a‑3p overexpression exerted proliferation‑suppressive and apoptosis‑stimulating effects on CC cells, whereas restoring CXCL8 attenuated the miR‑302c‑3p‑ and miR‑520a‑3p‑induced anti‑proliferative and pro‑apoptotic effects. miR‑302c‑3p and miR‑520a‑3p suppress the proliferation of CC cells by downregulating the expression of CXCL8, which may provide a novel target for the treatment of CC.
Keywords: cervical carcinoma; miR‑302c‑3p; miR‑520a‑3p; C‑X‑C motif ligand 8; proliferation; apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA‑130a‑3p promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via negative regulation of RUNX3.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Oct;22(4):2990-3000. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11368. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32945424
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00460 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by targeting microRNA-503-5p.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Dec;475(1-2):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03853-0. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32740791
-
miR-204 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting EphB2 in Human Cervical Cancer.Oncol Res. 2018 Jun 11;26(5):713-723. doi: 10.3727/096504017X15016337254641. Epub 2017 Aug 11. Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 28800788 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-628-5p Inhibits Cervical Carcinoma Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting VEGF.Am J Med Sci. 2021 Apr;361(4):499-508. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2020.11.031. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Am J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33775424
-
miRNAs role in cervical cancer pathogenesis and targeted therapy: Signaling pathways interplay.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Apr;244:154386. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154386. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36868096 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Chemokines in Cervical Cancers.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Oct 21;57(11):1141. doi: 10.3390/medicina57111141. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34833360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression miR-520a-3p inhibits acute myeloid leukemia progression via targeting MUC1.Transl Oncol. 2022 Aug;22:101432. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101432. Epub 2022 May 29. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35649317 Free PMC article.
-
The modulation of immune cell death in connection to microRNAs and natural products.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 20;15:1425602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425602. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39759512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-regulated transcripts with the potential to modulate human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte differentiation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Sep 2;13(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03138-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36056380 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Bushen Huoxue Decoction in Breast Cancer via Network Pharmacology and in vitro experiments.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025;21(1):50-66. doi: 10.2174/0115734099269728231115060827. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 39651565
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

