Research and application of hydrostatic high pressure in tumor vaccines (Review)
- PMID: 33760193
- PMCID: PMC8020208
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2021.8026
Research and application of hydrostatic high pressure in tumor vaccines (Review)
Abstract
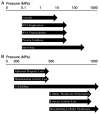
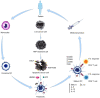
It is well known that hydrostatic pressure (HP) is a physical parameter that is now regarded as an important variable for life. High hydrostatic pressure (HHP) technology has influenced biological systems for more than 100 years. Food and bioscience researchers have shown great interest in HHP technology over the past few decades. The development of knowledge related to this area can better facilitate the application of HHP in the life sciences. Furthermore, new applications for HHP may come from these current studies, particularly in tumor vaccines. Currently, cancer recurrence and metastasis continue to pose a serious threat to human health. The limited efficacy of conventional treatments has led to the need for breakthroughs in immunotherapy and other related areas. Research into tumor vaccines is providing new insights for cancer treatment. The purpose of this review is to present the main findings reported thus far in the relevant scientific literature, focusing on knowledge related to HHP technology and tumor vaccines, and to demonstrate the potential of applying HHP technology to tumor vaccine development.
Keywords: hydrostatic high pressure; tumor vaccine; immunogenic cell death; dendritic cell; Annexin A5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High hydrostatic pressure in cancer immunotherapy and biomedicine.Biotechnol Adv. 2018 May-Jun;36(3):577-582. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Biotechnol Adv. 2018. PMID: 29409785 Review.
-
Generation of dendritic cell-based vaccine using high hydrostatic pressure for non-small cell lung cancer immunotherapy.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 10;12(2):e0171539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171539. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28187172 Free PMC article.
-
High hydrostatic pressure affects antigenic pool in tumor cells: Implication for dendritic cell-based cancer immunotherapy.Immunol Lett. 2017 Jul;187:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 8. Immunol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28495513
-
Dendritic cells pulsed with tumor cells killed by high hydrostatic pressure induce strong immune responses and display therapeutic effects both in murine TC-1 and TRAMP-C2 tumors when combined with docetaxel chemotherapy.Int J Oncol. 2016 Mar;48(3):953-64. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3314. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26718011 Free PMC article.
-
Microorganisms under high pressure--adaptation, growth and biotechnological potential.Biotechnol Adv. 2013 Dec;31(8):1426-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Biotechnol Adv. 2013. PMID: 23831003 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress in inducing immunogenic cell death of tumor cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1017400. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1017400. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of high hydrostatic pressure on the cytokine profile and head and neck cancer cell behavior: implications for oncological safety.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 28;16:1581014. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1581014. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40791595 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics and Paraprobiotics: Effects on Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Their Consequent Potential in Neuropsychiatric Therapy.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Aug;16(4):1440-1464. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10214-6. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 38294675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoover DG, Farka DF. Biological effects of high hydrostatic pressure on food microorganisms. Food Technol. 1989;43:99–107.
-
- Komora N, Maciel C, Pinto CA, Ferreira V, Brandão TRS, Saraiva JMA, Castro SM, Teixeira P. Non-thermal approach to Listeria monocytogenes inactivation in milk: The combined effect of high pressure, pediocin PA-1 and bacteriophage P100. Food Microbiol. 2020;86:103315. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2019.103315. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kurosaka G, Uemura S, Mochizuki T, Kozaki Y, Hozumi A, Suwa S, Ishii R, Kato Y, Imura S, Ishida N, et al. A novel ER membrane protein Ehg1/May24 plays a critical role in maintaining multiple nutrient permeases in yeast under high-pressure perturbation. Sci Rep. 2019;9:18341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54925-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

