Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering in real-world patients treated with evolocumab
- PMID: 33760276
- PMCID: PMC8119857
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.23600
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol lowering in real-world patients treated with evolocumab
Abstract
Background: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) is a risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). There are limited real-world data on LDL-C lowering with evolocumab in United States clinical practice.
Hypothesis: We assessed LDL-C lowering during 1 year of evolocumab therapy.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used linked laboratory (Prognos) and medical claims (IQVIA Dx/LRx and PharMetrics Plus® ) data. Patients with a first fill for evolocumab between 7/1/2015 and 10/31/2019 (index event) and LDL-C ≥ 70 mg/dL were included (overall cohort; N = 5897). Additionally, a patient subgroup with a recent myocardial infarction (MI) within 12 months (median 130 days) before the first evolocumab fill was identified (N = 152). Reduction from baseline LDL-C was calculated based on the lowest LDL-C value recorded during a 12-month follow-up period.
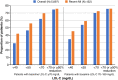
Results: The mean (SD) age was 65 (10) years; 61.9% of patients had ASCVD diagnoses and 70.7% of patients were in receipt of lipid-lowering therapy. Following evolocumab treatment, changes in LDL-C from baseline were -60% in the overall cohort (median [interquartile range (IQR)] 146 [115-180] mg/dL to 58 [36-84] mg/dL) and -65% in the recent MI subgroup (median [IQR] 137 [109-165] mg/dL to 48 [30-78] mg/dL). In the overall cohort and recent MI subgroup, 62.1% and 69.7% of patients achieved LDL-C < 70 mg/dL, respectively.
Conclusions: In this real-world analysis, evolocumab was associated with significant reductions in LDL-C comparable to that seen in the FOURIER clinical trial, which were durable over 1 year of treatment.
Keywords: LDL-C; atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; real-world evidence.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Cardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Nihar R. Desai reports research grants from Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson; consulting fees from Amgen Inc., Relypsa, OPKO, scPharmaceuticals, and Cytokinetics. Rolin L. Wade, Xin Wang, Chi‐Chang Chen are employees of IQVIA, which was hired by Amgen to conduct this study. Pin Xiang was an employee of Amgen Inc. when the study was conducted and is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim. Sasikiran Nunna was an employee of IQVIA when the study was conducted and is an employee of Bristol Myers Squibb. Lionel Pinto, Jason Exter, Katherine E. Mues, Mohdhar Habib are employees of Amgen Inc. and own Amgen stock.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LDL-C Reduction with Evolocumab Among Patients with ASCVD in China: Real-World Evidence from Tianjin Metropolitan Area.Adv Ther. 2025 Jun;42(6):2874-2887. doi: 10.1007/s12325-025-03199-3. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 40279014
-
A retrospective nationwide analysis of evolocumab use in Sweden and its effect on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.Ups J Med Sci. 2024 Jan 31;129. doi: 10.48101/ujms.v129.9618. eCollection 2024. Ups J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38327639 Free PMC article.
-
Evolocumab in HIV-Infected Patients With Dyslipidemia: Primary Results of the Randomized, Double-Blind BEIJERINCK Study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 May 26;75(20):2570-2584. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.03.025. Epub 2020 Mar 28. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32234462 Clinical Trial.
-
Recent Updates on the Use of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2019 Mar 16;21(5):16. doi: 10.1007/s11883-019-0778-6. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2019. PMID: 30877491 Review.
-
Lowering Targeted Atherogenic Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goals for Patients at "Extreme" ASCVD Risk.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Nov 21;19(12):146. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1246-y. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31754844 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-World Application of Evolocumab Among Patients with Hyperlipidemia in Korea: A Multicenter Prospective Study.Cardiol Ther. 2024 Dec;13(4):695-706. doi: 10.1007/s40119-024-00389-y. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Cardiol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39436637 Free PMC article.
-
LDL-C Reduction with Evolocumab Among Patients with ASCVD in China: Real-World Evidence from Tianjin Metropolitan Area.Adv Ther. 2025 Jun;42(6):2874-2887. doi: 10.1007/s12325-025-03199-3. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 40279014
-
Cardiovascular Outcomes of Early LDL-C Goal Achievement in Patients with Very-High-Risk ASCVD.Cardiol Ther. 2025 Mar;14(1):101-115. doi: 10.1007/s40119-025-00397-6. Epub 2025 Feb 23. Cardiol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39988704 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insights into the Management of Patients with Very High Cardiovascular Risk Eligible for PCSK9 Inhibitor Treatment: Baseline Findings from the PERI-DYS Study.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Feb;38(1):119-129. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07386-0. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 36178485 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Insights into Evolocumab Use in Patients with Hyperlipidemia Across Five Countries: Analysis from the ZERBINI Study.Cardiol Ther. 2023 Dec;12(4):703-722. doi: 10.1007/s40119-023-00334-5. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Cardiol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37804438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khavjou O, Phelps D, Leib A. Projections of cardiovascular disease prevalence and costs: 2015‐2035. https://healthmetrics.heart.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Projections-o... (accessed March 2020).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

