In vitro exploration of the Xanthomonas hortorum pv. vitians genome using transposon insertion sequencing and comparative genomics to discriminate between core and contextual essential genes
- PMID: 33760724
- PMCID: PMC8627662
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.000546
In vitro exploration of the Xanthomonas hortorum pv. vitians genome using transposon insertion sequencing and comparative genomics to discriminate between core and contextual essential genes
Abstract
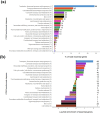
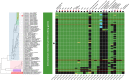
The essential genome of a bacterium encompasses core genes associated with basic cellular processes and conditionally essential genes dependent upon environmental conditions or the genetic context. Comprehensive knowledge of those gene sets allows for a better understanding of fundamental bacterial biology and offers new perspectives for antimicrobial drug research against detrimental bacteria such as pathogens. We investigated the essential genome of Xanthomonas hortorum pv. vitians, a gammaproteobacterial plant pathogen of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) which belongs to the plant-pathogen reservoir genus Xanthomonas and is affiliated to the family Xanthomonadaceae. No practical means of disease control or prevention against this pathogen is currently available, and its molecular biology is virtually unknown. To reach a comprehensive overview of the essential genome of X. hortorum pv. vitians LM16734, we developed a mixed approach combining high-quality full genome sequencing, saturated transposon insertion sequencing (Tn-Seq) in optimal growth conditions, and coupled computational analyses such as comparative genomics, synteny assessment and phylogenomics. Among the 370 essential loci identified by Tn-Seq, a majority was bound to critical cell processes conserved across bacteria. The remaining genes were either related to specific ecological features of Xanthomonas or Xanthomonadaceae species, or acquired through horizontal gene transfer of mobile genetic elements and associated with ancestral parasitic gene behaviour and bacterial defence systems. Our study sheds new light on our usual concepts about gene essentiality and is pioneering in the molecular and genomic study of X. hortorum pv. vitians.
Keywords: Tn-Seq; Xanthomonadaceae; Xanthomonas hortorum; bacterial leaf spot of lettuce; essential genome; mobile genetic elements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

