Distinct features of the Leishmania cap-binding protein LeishIF4E2 revealed by CRISPR-Cas9 mediated hemizygous deletion
- PMID: 33760809
- PMCID: PMC8021392
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008352
Distinct features of the Leishmania cap-binding protein LeishIF4E2 revealed by CRISPR-Cas9 mediated hemizygous deletion
Abstract
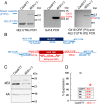
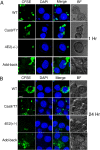
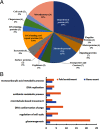
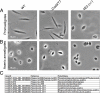
Leishmania parasites cycle between sand-fly vectors and mammalian hosts adapting to alternating environments by stage-differentiation accompanied by changes in the proteome profiles. Translation regulation plays a central role in driving the differential program of gene expression since control of gene regulation in Leishmania is mostly post-transcriptional. The Leishmania genome encodes six eIF4E paralogs, some of which bind a dedicated eIF4G candidate, and each eIF4E is assumed to have specific functions with perhaps some overlaps. However, LeishIF4E2 does not bind any known eIF4G ortholog and was previously shown to comigrate with the polysomal fractions of sucrose gradients in contrast to the other initiation factors that usually comigrate with pre-initiation and initiation complexes. Here we deleted one of the two LeishIF4E2 gene copies using the CRISPR-Cas9 methodology. The deletion caused severe alterations in the morphology of the mutant cells that became round, small, and equipped with a very short flagellum that did not protrude from its pocket. Reduced expression of LeishIF4E2 had no global effect on translation and growth, unlike other LeishIF4Es; however, there was a change in the proteome profile of the LeishIF4E2(+/-) cells. Upregulated proteins were related mainly to general metabolic processes including enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism, DNA repair and replication, signaling, and cellular motor activity. The downregulated proteins included flagellar rod and cytoskeletal proteins, as well as surface antigens involved in virulence. Moreover, the LeishIF4E2(+/-) cells were impaired in their ability to infect cultured macrophages. Overall, LeishIF4E2 does not behave like a general translation factor and its function remains elusive. Our results also suggest that the individual LeishIF4Es perform unique functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

