Is the heart rate variability monitoring using the analgesia nociception index a predictor of illness severity and mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19? A pilot study
- PMID: 33760875
- PMCID: PMC7990300
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249128
Is the heart rate variability monitoring using the analgesia nociception index a predictor of illness severity and mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19? A pilot study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Is the heart rate variability monitoring using the analgesia nociception index a predictor of illness severity and mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19? A pilot study.PLoS One. 2021 May 20;16(5):e0252259. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252259. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34015062 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: The analysis of heart rate variability (HRV) has proven to be an important tool for the management of autonomous nerve system in both surgical and critically ill patients. We conducted this study to show the different spectral frequency and time domain parameters of HRV as a prospective predictor for critically ill patients, and in particular for COVID-19 patients who are on mechanical ventilation. The hypothesis is that most severely ill COVID-19 patients have a depletion of the sympathetic nervous system and a predominance of parasympathetic activity reflecting the remaining compensatory anti-inflammatory response.
Materials and methods: A single-center, prospective, observational pilot study which included COVID-19 patients admitted to the Surgical Intensive Care Unit was conducted. The normalized high-frequency component (HFnu), i.e. ANIm, and the standard deviation of RR intervals (SDNN), i.e. Energy, were recorded using the analgesia nociception index monitor (ANI). To estimate the severity and mortality we used the SOFA score and the date of discharge or date of death.
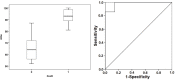
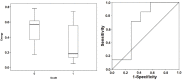
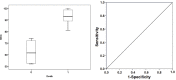
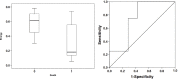
Results: A total of fourteen patients were finally included in the study. ANIm were higher in the non-survivor group (p = 0.003) and were correlated with higher IL-6 levels (p = 0.020). Energy was inversely correlated with SOFA (p = 0.039) and fewer survival days (p = 0.046). A limit value at 80 of ANIm, predicted mortalities with a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 85.7%. In the case of Energy, a limit value of 0.41 ms predicted mortality with all predictive values of 71.4%.
Conclusion: A low autonomic nervous system activity, i.e. low SDNN or Energy, and a predominance of the parasympathetic system, i.e. low HFnu or ANIm, due to the sympathetic depletion in COVID-19 patients are associated with a worse prognosis, higher mortality, and higher IL-6 levels.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest on the part of any author.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analgesia nociception index and high frequency variability index: promising indicators of relative parasympathetic tone.J Anesth. 2023 Feb;37(1):130-137. doi: 10.1007/s00540-022-03126-8. Epub 2022 Oct 22. J Anesth. 2023. PMID: 36272031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospective multicenter study of heart rate variability with ANI monitor as predictor of mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 16;12(1):21762. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25537-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36526646 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesia nociception index for the assessment of pain in critically ill patients: a diagnostic accuracy study.Br J Anaesth. 2017 Oct 1;119(4):812-820. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex210. Br J Anaesth. 2017. PMID: 29121287
-
Effects of hypnosis on the relative parasympathetic tone assessed by ANI (Analgesia/Nociception Index) in healthy volunteers: a prospective observational study.J Clin Monit Comput. 2018 Jun;32(3):487-492. doi: 10.1007/s10877-017-0056-5. Epub 2017 Aug 20. J Clin Monit Comput. 2018. PMID: 28825157
-
Electrophisiological monitoring of pain in non-communicative critically ill patients.Enferm Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2025 Jan-Mar;36(1):100489. doi: 10.1016/j.enfie.2024.100489. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Enferm Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2025. PMID: 39827496 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Autonomic Function in Long COVID-19 Using Heart Rate Variability: An Observational Cross-Sectional Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 22;12(1):100. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010100. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36614901 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Heart Rate Variability: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies with Control Groups.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 4;20(2):909. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20020909. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673664 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate variability comparison between young males after 4-6 weeks from the end of SARS-CoV-2 infection and controls.Sci Rep. 2022 May 25;12(1):8832. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12844-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35614330 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesia nociception index and high frequency variability index: promising indicators of relative parasympathetic tone.J Anesth. 2023 Feb;37(1):130-137. doi: 10.1007/s00540-022-03126-8. Epub 2022 Oct 22. J Anesth. 2023. PMID: 36272031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of COVID-19 on Stress and Biomarkers: An Exploratory Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2023 Mar 2;15(3):e35702. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35702. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37016651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lazzerini PE, Boutjdir M, Capecchi PL. COVID-19, Arrhythmic Risk and Inflammation: Mind the Gap! Circulation 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

