Membrane-cytoplasm translocation of annexin A4 is involved in the metastasis of colorectal carcinoma
- PMID: 33761465
- PMCID: PMC8064178
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202793
Membrane-cytoplasm translocation of annexin A4 is involved in the metastasis of colorectal carcinoma
Abstract
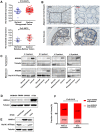
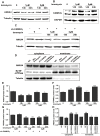
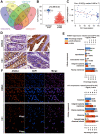
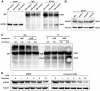
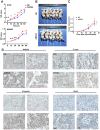
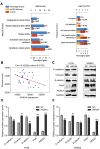
Annexin A4 (ANXA4) is a Ca2+- and phospholipid-binding protein that belongs to the annexin family, which is involved in the development of multiple tumour types via NF-κB signalling. In this study, we verified the high expression and membrane-cytoplasm translocation of ANXA4 in colorectal carcinoma (CRC). Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II gamma (CAMK2γ) was found to be important for high ANXA4 expression in CRC, whereas carbonic anhydrase (CA1) promoted ANXA4 aggregation in the cell membrane. An increased Ca2+ concentration attenuated the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of cytoplasmic ANXA4 and ANXA4 stabilization, and relatively high expression of ANXA4 promoted CRC tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Keywords: SUMO; annexin A4; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II gamma; carbonic anhydrase; membrane-cytoplasm translocation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

