Epidemiology of asymptomatic and symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 confirmed cases in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: Observational study
- PMID: 33761710
- PMCID: PMC9282025
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025219
Epidemiology of asymptomatic and symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 confirmed cases in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: Observational study
Abstract
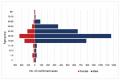
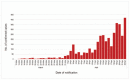
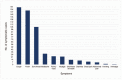
This study was conducted to describe demographics, clinical features, and outcomes of 3827 confirmed cases of Coronavirus Disease 2019 between March 12 and April 22, 2020 in the Emirates of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates (UAE).Data were extracted from the Infectious Diseases Notification Surveillance System of the Department of Health. The descriptive analysis was done using Statistical Package for Social Sciences v26 and reported according to Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement.We analyzed 3827 cases; 82% were men, 18% women, 14% UAE citizens, and 86% were of other nationalities. Most cases (72%) had lower exposure to low-risk occupations of infectious disease as per the classification of the department of health while high exposure risk occupations, which included healthcare worker accounts only for 3%. While 43% of cases were asymptomatic, 57% displayed symptoms, which were mostly mild. Only 12% of patients had comorbidities, which were significantly higher in men (9%) than women (3%). Among those who have comorbid conditions; hypertension (27%) and diabetes (21%) were the most common comorbidities. Viral pneumonia (11%) was the most common sequela documented in records. Only 51 patients (4%) required admission to the intensive care units, and 4 patients died (0.1%).The significant number of asymptomatic patients was identified by active case finding and contact tracing from the early period of the epidemic. A small percentage of severe, critical cases, and death reported in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi which may have been due to public health measures implemented for early detection, contact tracing, and treatment.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Phelan AL, Katz R, Gostin LO. The novel coronavirus originating in Wuhan, China: challenges for Global Health Governance. JAMA 2020;323:709–10. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO/Europe Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak - about the virus; 2020. Available at: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-.... Accessed April 27, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

