Lung compartmentalization of inflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19-related ARDS
- PMID: 33761985
- PMCID: PMC7988241
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03513-9
Lung compartmentalization of inflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19-related ARDS
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests to declare.
Figures
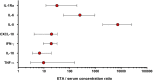
Comment on
-
Alveolar compartmentalization of inflammatory and immune cell biomarkers in pneumonia-related ARDS.Crit Care. 2021 Jan 9;25(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03427-y. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33422148 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

