TDP-43 proteinopathy alters the ribosome association of multiple mRNAs including the glypican Dally-like protein (Dlp)/GPC6
- PMID: 33762006
- PMCID: PMC7992842
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-021-01148-z
TDP-43 proteinopathy alters the ribosome association of multiple mRNAs including the glypican Dally-like protein (Dlp)/GPC6
Abstract
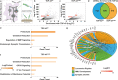
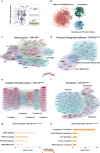
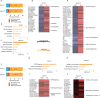
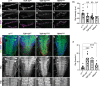
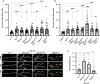
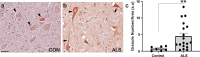
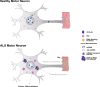
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a genetically heterogeneous neurodegenerative disease in which 97% of patients exhibit cytoplasmic aggregates containing the RNA binding protein TDP-43. Using tagged ribosome affinity purifications in Drosophila models of TDP-43 proteinopathy, we identified TDP-43 dependent translational alterations in motor neurons impacting the spliceosome, pentose phosphate and oxidative phosphorylation pathways. A subset of the mRNAs with altered ribosome association are also enriched in TDP-43 complexes suggesting that they may be direct targets. Among these, dlp mRNA, which encodes the glypican Dally like protein (Dlp)/GPC6, a wingless (Wg/Wnt) signaling regulator is insolubilized both in flies and patient tissues with TDP-43 pathology. While Dlp/GPC6 forms puncta in the Drosophila neuropil and ALS spinal cords, it is reduced at the neuromuscular synapse in flies suggesting compartment specific effects of TDP-43 proteinopathy. These findings together with genetic interaction data show that Dlp/GPC6 is a novel, physiologically relevant target of TDP-43 proteinopathy.
Keywords: ALS; Drosophila; Glypican; Motor neuron; Neuromuscular junction; TDP-43; Translation; Wnt signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
DCZ is a Scientific Advisor for Fox Chase Chemical Diversity Center, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modelling TDP-43 proteinopathy in Drosophila uncovers shared and neuron-specific targets across ALS and FTD relevant circuits.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Oct 20;11(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01656-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37864255 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of autophagy mitigates TDP-43 pathology and translational repression of neurofilament mRNAs in mouse models of ALS/FTD.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Jan 7;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00420-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 33413517 Free PMC article.
-
Motor neuron TDP-43 proteinopathy in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration.Brain. 2022 Aug 27;145(8):2769-2784. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac091. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35274674
-
Disease animal models of TDP-43 proteinopathy and their pre-clinical applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Oct 9;14(10):20079-111. doi: 10.3390/ijms141020079. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24113586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TDP-43 proteinopathy and mitochondrial abnormalities in neurodegeneration.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2019 Oct;100:103396. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2019.103396. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31445085 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Translation dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: a focus on ALS.Mol Neurodegener. 2023 Aug 25;18(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00642-3. Mol Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 37626421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal models of TDP-43 proteinopathy display reduced axonal translation, increased oxidative stress, and defective exocytosis.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 13;17:1253543. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1253543. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38026702 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling TDP-43 proteinopathy in Drosophila uncovers shared and neuron-specific targets across ALS and FTD relevant circuits.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Oct 20;11(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01656-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37864255 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome-associated pathological TDP-43 alters the expression of multiple mRNAs in the monkey brain.Zool Res. 2025 Mar 18;46(2):263-276. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.286. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 39973136 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanisms underlying TDP-43-associated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related dementias.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jun 25. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03089-8. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40562864 Review.
References
-
- Arnold ES, Ling SC, Huelga SC, Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Ditsworth D, Kordasiewicz HB, McAlonis-Downes M, Platoshyn O, Parone PA, et al. ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:E736–745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222809110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakkar N, Kovalik T, Lorenzini I, Spangler S, Lacoste A, Sponaugle K, Ferrante P, Argentinis E, Sattler R, Bowser R. Artificial intelligence in neurodegenerative disease research: use of IBM Watson to identify additional RNA-binding proteins altered in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2018;135:227–247. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1785-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

