The expansive effects of polyamines on the metabolism and virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 33762024
- PMCID: PMC7990898
- DOI: 10.1186/s41479-021-00082-x
The expansive effects of polyamines on the metabolism and virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
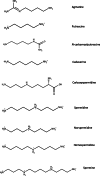
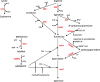
Polyamines are common intracellular metabolites of nearly all cells, and their conservation across a vast diversity of cells suggests critical roles for these compounds in cellular physiology. Most intracellular polyamines are associated with RNA and, subsequently, polyamines have significant effects on transcription and translation. Putrescine and spermidine are the most common polyamines in bacteria. Intracellular polyamine pools in bacteria are tightly controlled by both de novo synthesis and transport. Polyamine homeostasis is emerging as a critical parameter of multiple pathways and physiology with substantial impact on bacterial pathogenesis, including the important human pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. Modulation of polyamine metabolism in pneumococci is an important regulator of central metabolism. It has broad effects on virulence factors such as capsule as well as stress responses that ultimately impact the survival of pneumococcus in a host. Polyamine transport protein as a single antigen or in combination with other pneumococcal proteins is shown to be an efficacious immunogen that protects against nasopharyngeal colonization, and invasive disease. A comprehensive description of polyamine metabolic pathways and their intersection with pneumococcal pathogenesis will undoubtedly point to novel approaches for treatment and prevention of pneumococcal disease.
Keywords: Autolysis; Capsule; Immunization; Pneumococci; Polyamine; PotD; Stress response; Virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared. We requested replacing/modifying current
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polyamine biosynthesis and transport mechanisms are crucial for fitness and pathogenesis of Streptococcus pneumoniae.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Feb;157(Pt 2):504-515. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.042564-0. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 20966092
-
Role of polyamine transport in Streptococcus pneumoniae response to physiological stress and murine septicemia.Microb Pathog. 2008 Sep;45(3):167-72. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2008.05.001. Epub 2008 May 16. Microb Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18572376
-
Involvement of potD in Streptococcus pneumoniae polyamine transport and pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2006 Jan;74(1):352-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.352-361.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16368990 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary and Gut Microbiota Polyamines in Obesity- and Age-Related Diseases.Front Nutr. 2019 Mar 14;6:24. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00024. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30923709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyamine metabolism in different pathological states of the brain.Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1992 Jun;16(3):241-71. doi: 10.1007/BF03159973. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1992. PMID: 1358085 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Difluoromethylornithine and AMXT 1501 on Gene Expression and Capsule Regulation in Streptococcus pneumoniae.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 2;14(2):178. doi: 10.3390/biom14020178. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397415 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines: Functions, Metabolism, and Role in Human Disease Management.Med Sci (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;9(2):44. doi: 10.3390/medsci9020044. Med Sci (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of fluid shear stress on oral biofilm formation and composition and the transcriptional response of Streptococcus gordonii.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2024 Dec;39(6):477-490. doi: 10.1111/omi.12481. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39158270 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and diversity of classical deacylases in bacteria.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 3;15(1):9496. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53903-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39489725 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an Arginine Decarboxylase from Streptococcus pneumoniae by Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Biomolecules. 2024 Apr 10;14(4):463. doi: 10.3390/biom14040463. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Brien KL, Wolfson LJ, Watt JP, Henkle E, Deloria-Knoll M, McCall N, Lee E, Mulholland K, Levine OS, Cherian T. Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates. Lancet. 2009;374(9693):893–902. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61204-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Organization WH. Top 10 Causes of Death 2020 [Available from: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of....
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

