Positive Controls in Adults and Children Support That Very Few, If Any, New Neurons Are Born in the Adult Human Hippocampus
- PMID: 33762407
- PMCID: PMC8018729
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0676-20.2020
Positive Controls in Adults and Children Support That Very Few, If Any, New Neurons Are Born in the Adult Human Hippocampus
Abstract
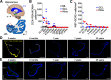
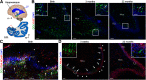
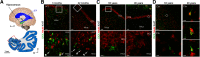
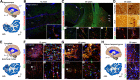
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis was originally discovered in rodents. Subsequent studies identified the adult neural stem cells and found important links between adult neurogenesis and plasticity, behavior, and disease. However, whether new neurons are produced in the human dentate gyrus (DG) during healthy aging is still debated. We and others readily observe proliferating neural progenitors in the infant hippocampus near immature cells expressing doublecortin (DCX), but the number of such cells decreases in children and few, if any, are present in adults. Recent investigations using dual antigen retrieval find many cells stained by DCX antibodies in adult human DG. This has been interpreted as evidence for high rates of adult neurogenesis, even at older ages. However, most of these DCX-labeled cells have mature morphology. Furthermore, studies in the adult human DG have not found a germinal region containing dividing progenitor cells. In this Dual Perspectives article, we show that dual antigen retrieval is not required for the detection of DCX in multiple human brain regions of infants or adults. We review prior studies and present new data showing that DCX is not uniquely expressed by newly born neurons: DCX is present in adult amygdala, entorhinal and parahippocampal cortex neurons despite being absent in the neighboring DG. Analysis of available RNA-sequencing datasets supports the view that DG neurogenesis is rare or absent in the adult human brain. To resolve the conflicting interpretations in humans, it is necessary to identify and visualize dividing neuronal precursors or develop new methods to evaluate the age of a neuron at the single-cell level.
Keywords: aging; dentate gyrus; doublecortin; human hippocampus; neural progenitors; neurogenesis; new neurons.
Copyright © 2021 the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Ambrogini P, Lattanzi D, Ciuffoli S, Agostini D, Bertini L, Stocchi V, Santi S, Cuppini R (2004) Morpho-functional characterization of neuronal cells at different stages of maturation in granule cell layer of adult rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res 1017:21–31. 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.05.039 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
