Comparative Antibody Responses to the Live-Attenuated and Recombinant Herpes Zoster Vaccines
- PMID: 33762414
- PMCID: PMC8316136
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00240-21
Comparative Antibody Responses to the Live-Attenuated and Recombinant Herpes Zoster Vaccines
Abstract
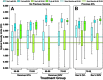
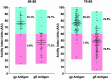
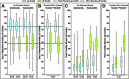
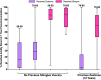
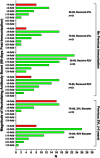
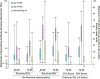
Two herpes zoster (HZ) vaccines licensed in the United States are recommended by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP): (i) live-attenuated vaccine (ZVL) using vOka strain varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and (ii) recombinant adjuvanted vaccine (RZV) containing recombinant varicella-zoster virus (VZV) glycoprotein E (gE). Two phase 3 clinical trials of RZV led the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) to recommend it with preferred status. VZV T cell-mediated immunity (CMI), but not humoral immunity, is considered essential for protection against HZ. Published studies of humoral immunity focused on VZV-specific IgG concentration. To complement reports comparing the CMI responses to these vaccines, we compared humoral responses in ZVL and RZV recipients, emphasizing functional qualities (avidity and neutralization). Baseline avidities to a VZV glycoprotein mixture (gp) were near the upper limit of detection, but avidity to gE was much lower. Small increases in gp avidity were observed for both RZV and ZVL vaccination (19 and 12 avidity index units [AIU], respectively). RZV boosted both gE avidity and VZV neutralizing antibody significantly more than ZVL (mean gE avidity boost, 47 AIU versus 22 AIU; mean neutralizing antibody boost, 22-fold versus 8-fold). Increases in neutralizing antibodies strongly correlated with gE avidity increases (r = 0.5) and moderately with gp avidity increases (r = 0.23). After 1 year, 81% of RZV recipients and only 18% of ZVL recipients retained >50% of their peak avidity boosts. These results are consistent with the CMI responses to these vaccines: RZV responses are skewed to long-term memory, whereas ZVL preferentially induces transient effector responses.IMPORTANCE These observations further distinguish the immunogenicity and duration of the immune response of the two vaccines. In addition, measurements of functional humoral immunity (IgG avidity and neutralizing antibody) in response to zoster immunization, alone or combined with other immune markers, might contribute to practical in vitro correlates of protection. Combined with previous observations of the cell-mediated response to these vaccines, this study suggests that vaccine development will benefit from more expansive and granular assessments of acquired immunity during early phase 1 immunogenicity trials.
Keywords: avidity; herpes zoster; humoral immunity; neutralizing antibodies; vaccine.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Levin MJ. 2017. Zoster vaccine, p 1268–1281. In Plotkin S, Orenstein W, Offitt P, Edwards KM (ed), Vaccines, 7th ed. Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Levin MJ, Schmader KS, Oxman MN. 2019. Chapter 165. Varicella and herpes zoster, p 3035–3064. In Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, Enk AH, Margolis DJ, McMichael AJ, Orringer JS (ed), Fitzpatrick’s dermatology, 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education, New York, NY.
-
- Weinberg A, Lazar AA, Zerbe GO, Hayward AR, Chan IS, Vessey R, Silber JL, MacGregor RR, Chan K, Gershon AA, Levin MJ. 2010. Influence of age and nature of primary infection on varicella-zoster virus-specific cell-mediated immune responses. J Infect Dis 201:1024–1030. 10.1086/651199. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

