The DJ1-Nrf2-STING axis mediates the neuroprotective effects of Withaferin A in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 33762743
- PMCID: PMC8329302
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-021-00767-2
The DJ1-Nrf2-STING axis mediates the neuroprotective effects of Withaferin A in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
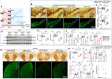
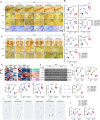
The pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD) remains unclear, and there is no disease-modifying agent for PD. Withaferin A (WA), a naturally occurring compound, has emerged as a neuroprotective agent. However, the mechanisms by which WA is neuroprotective in PD are unknown. Here we show that WA protected against loss of dopaminergic neurons, neuroinflammation, and motor deficits in MPTP-induced PD mouse models. Whole-genome deep sequencing analysis combined with Meta-analysis of human PD studies reveal that DJ1, Nrf2, and STING in substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) are linked to anti-PD effect of WA. We found that WA activated DJ1 and Nrf2, and suppressed STING within SNc; and overexpression of STING in SNc dampened the effect of WA. Using genetically modified mice (DJ1-KO, Nrf2-KO, STINGgt/gt and STING-KO) and immunolabeling technique, we identified that WA targeted DJ1-Nrf2-STING pathway in dopaminergic neurons; and we demonstrate that STING might be an important factor in PD pathogenesis. In addition, WA alleviated accumulation of phosphorylated α-synuclein (p-α-syn) and insoluble α-syn within SNc in adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated human α-syn overexpression PD model. Our comparative analysis on whole-genome transcriptome profiles suggests that STING might be a key target of WA and amantadine in PD treatment. This study highlights a multifaceted role for WA in neuroprotection, and suggests that WA can be a potential candidate for treatment of PD.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to ADMC Associazione Differenziamento e Morte Cellulare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Nrf2-NLRP3-caspase-1 axis mediates the neuroprotective effects of Celastrol in Parkinson's disease.Redox Biol. 2021 Nov;47:102134. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102134. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Redox Biol. 2021. PMID: 34600334 Free PMC article.
-
Bruceine D elevates Nrf2 activation to restrain Parkinson's disease in mice through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory response.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 11;526(4):1013-1020. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.097. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32321640
-
Neuroprotective effects of protocatechuic aldehyde through PLK2/p-GSK3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway in both in vivo and in vitro models of Parkinson's disease.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Nov 6;11(21):9424-9441. doi: 10.18632/aging.102394. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31697645 Free PMC article.
-
The principal molecular mechanisms behind the activation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway leading to neuroprotective action in Parkinson's disease.Neurochem Int. 2022 Jun;156:105325. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105325. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Neurochem Int. 2022. PMID: 35278519 Review.
-
Role of Astrogliosis in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease: Insights into Astrocytic Nrf2 Pathway as a Potential Therapeutic Target.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(8):1015-1029. doi: 10.2174/0118715273270473231002104610. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37817521 Review.
Cited by
-
Withaferin A inhibits ferroptosis and protects against intracerebral hemorrhage.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jun;18(6):1308-1315. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.355822. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36453416 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like Growth Factor II Prevents MPP+ and Glucocorticoid Mitochondrial-Oxidative and Neuronal Damage in Dopaminergic Neurons.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 24;11(1):41. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010041. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052545 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodegeneration and Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's Disease: a Self-Sustained Loop.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2022 Aug;22(8):427-440. doi: 10.1007/s11910-022-01207-5. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35674870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferulic Acid Interferes with Radioactive Intestinal Injury Through the DJ-1-Nrf2 and Sirt1-NF-κB-NLRP3 Pathways.Molecules. 2024 Oct 26;29(21):5072. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215072. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519712 Free PMC article.
-
PARK7/DJ-1 in microglia: implications in Parkinson's disease and relevance as a therapeutic target.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Apr 18;20(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02776-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37072827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

