Persistent Globe Flattening in Astronauts following Long-Duration Spaceflight
- PMID: 33762785
- PMCID: PMC7946045
- DOI: 10.1080/01658107.2020.1791189
Persistent Globe Flattening in Astronauts following Long-Duration Spaceflight
Abstract
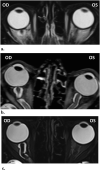
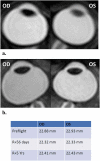
Posterior globe flattening has been well-documented in astronauts both during and after long-duration space flight (LDSF) and has been observed as early as 10 days into a mission on the International Space Station. Globe flattening (GF) is thought to be caused by the disc centred anterior forces created by elevated volume and/or pressure within the optic nerve sheath (ONS). This might be the result of increased intracranial pressure, increased intraorbital ONS pressure from compartmentalisation or a combination of these mechanisms. We report posterior GF in three astronauts that has persisted for 7 years or more following their return from LDSFs suggesting that permanent scleral remodelling may have occurred.
Keywords: SANS; astronaut; hyperopic shift; international space station (ISS); long-duration space flight (LDSF); visual changes.
© 2020 Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Figures
References
-
- NASA Lifetime Surveillance of Astronaut Health (LSAH). Houston, Texas: NASA Johnson Space Center; 2018. May.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
