Dysregulation of MicroRNAs and PIWI-Interacting RNAs in a Caenorhabditis elegans Parkinson's Disease Model Overexpressing Human α-Synuclein and Influence of tdp-1
- PMID: 33762903
- PMCID: PMC7982545
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.600462
Dysregulation of MicroRNAs and PIWI-Interacting RNAs in a Caenorhabditis elegans Parkinson's Disease Model Overexpressing Human α-Synuclein and Influence of tdp-1
Abstract
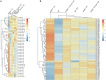
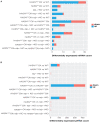
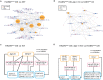
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) regulate gene expression and biological processes through specific genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. Recent studies have described a dysregulation of small non-coding RNAs in Parkinson's disease (PD) tissues but have been limited in scope. Here, we extend these studies by comparing the dysregulation of both miRNAs and piRNAs from transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) nematodes overexpressing pan-neuronally human α-synuclein wild-type (WT) (HASNWT OX) or mutant (HASNA53T OX). We observed 32 miRNAs and 112 piRNAs dysregulated in HASNA53T OX compared with WT. Genetic crosses of HASNA53T OX PD animal models with tdp-1 null mutants, the C. elegans ortholog of TDP-43, an RNA-binding protein aggregated in frontal temporal lobar degeneration, improved their behavioral deficits and changed the number of dysregulated miRNAs to 11 and piRNAs to none. Neuronal function-related genes T28F4.5, C34F6.1, C05C10.3, camt-1, and F54D10.3 were predicted to be targeted by cel-miR-1018, cel-miR-355-5p (C34F6.1 and C05C10.3), cel-miR-800-3p, and 21ur-1581 accordingly. This study provides a molecular landscape of small non-coding RNA dysregulation in an animal model that provides insight into the epigenetic changes, molecular processes, and interactions that occur during PD-associated neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; PIWI-interacting RNA; microRNA; neurodegenerative disease; synucleinopathies.
Copyright © 2021 Shen, Wang, Chen and Wong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

