Cinical, Metabolic, and Genetic Analysis and Follow-Up of Eight Patients With HIBCH Mutations Presenting With Leigh/Leigh-Like Syndrome
- PMID: 33762937
- PMCID: PMC7982470
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.605803
Cinical, Metabolic, and Genetic Analysis and Follow-Up of Eight Patients With HIBCH Mutations Presenting With Leigh/Leigh-Like Syndrome
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Cinical, Metabolic, and Genetic Analysis and Follow-Up of Eight Patients With HIBCH Mutations Presenting With Leigh/Leigh-Like Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 10;12:686933. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.686933. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34177596 Free PMC article.
Abstract
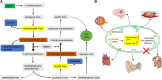
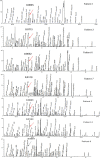
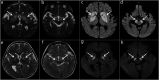
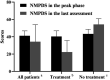
3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA hydrolase (HIBCH, NM_014362.3) gene mutation can cause HIBCH deficiency, leading to Leigh/Leigh-like disease. To date, few case series have investigated the relationship between metabolites and clinical phenotypes or the effects of treatment, although 34 patients with HIBCH mutations from 27 families have been reported. The purpose of this study was to analyze the phenotypic spectrum, follow-up results, metabolites, and genotypes of patients with HIBCH deficiency presenting with Leigh/Leigh-like syndrome and explore specific metabolites related to disease diagnosis and prognosis through retrospective and longitudinal studies. Applying next-generation sequencing, we identified eight patients with HIBCH mutations from our cohort of 181 cases of genetically diagnosed Leigh/Leigh-like syndrome. Six novel HIBCH mutations were identified: c.977T>G [p.Leu326Arg], c.1036G>T [p.Val346Phe], c.750+1G>A, c.810-2A>C, c.469C>T [p.Arg157*], and c.236delC [p.Pro79Leufs*5]. The Newcastle Pediatric Mitochondrial Disease Scale (NPMDS) was employed to assess disease progression and clinical outcomes. The non-invasive approach of metabolite analysis showed that levels of some were associated with clinical phenotype severity. Five (5/7) patients presented with elevated C4-OH in dried blood spots, and the level was probably correlated with the NPMDS scores during the peak disease phase. 2,3-Dihydroxy-2-methylbutyrate in urine was elevated in six (6/7) patients and elevated S-(2-caboxypropyl)cysteamine in urine was found in three patients (3/3). The median age at initial presentation was 13 months (8-18 months), and the median follow-up was 2.3 years (range 1.3-7.2 years). We summarized and compared with all reported patients with HIBCH mutations. The most prominent clinical manifestations were developmental regression/delay, hypotonia, encephalopathy, and feeding difficulties. We administered drug and dietary treatment. During follow-up, five patients responded positively to treatment with a significant decrease in NPMDS scores. Our research is the largest case series of patients with HIBCH mutations.
Keywords: 2,3-dihydroxy-2-methylbutyrate (23DH2MB); C4-OH; HIBCH gene; Leigh/Leigh-like syndrome; children; mitochondrial disorders.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Liu, Xu, Han, Ren, Yang, Zhang and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
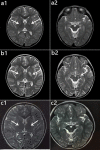
Figures

References
-
- Candelo E., Cochard L., Caicedo-Herrera G., Granados A. M., Gomez J. F., Díaz-Ordoñez L., et al. (2019). Syndromic progressive neurodegenerative disease of infancy caused by novel variants in HIBCH: report of two cases in Colombia. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 8 (3), 187–193. 10.5582/irdr.2019.01014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

