Synedrella nodiflora Extract Depresses Excitatory Synaptic Transmission and Chemically-Induced In Vitro Seizures in the Rat Hippocampus
- PMID: 33762938
- PMCID: PMC7982396
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.610025
Synedrella nodiflora Extract Depresses Excitatory Synaptic Transmission and Chemically-Induced In Vitro Seizures in the Rat Hippocampus
Abstract
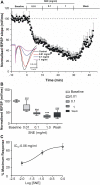
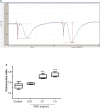
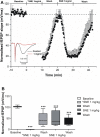
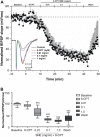
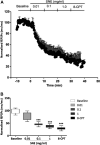
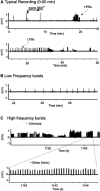
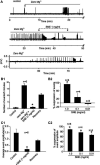
Extracts of the tropical Cinderella plant Synedrella nodiflora are used traditionally to manage convulsive conditions in the West African sub-region. This study sought to determine the neuronal basis of the effectiveness of these plant extracts to suppress seizure activity. Using the hippocampal slice preparation from rats, the ability of the extract to depress excitatory synaptic transmission and in vitro seizure activity were investigated. Bath perfusion of the hydro-ethanolic extract of Synedrella nodiflora (SNE) caused a concentration-dependent depression of evoked field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) recorded extracellularly in the CA1 region of the hippocampus with maximal depression of about 80% and an estimated IC50 of 0.06 mg/ml. The SNE-induced fEPSP depression was accompanied by an increase in paired pulse facilitation. The fEPSP depression only recovered partially after 20 min washing out. The effect of SNE was not stimulus dependent as it was present even in the absence of synaptic stimulation. Furthermore, it did not show desensitization as repeat application after 10 min washout produced the same level of fEPSP depression as the first application. The SNE effect on fEPSPs was not via adenosine release as it was neither blocked nor reversed by 8-CPT, an adenosine A1 receptor antagonist. In addition, SNE depressed in vitro seizures induced by zero Mg2+ and high K+ -containing artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) in a concentration-dependent manner. The results show that SNE depresses fEPSPs and spontaneous bursting activity in hippocampal neurons that may underlie its ability to abort convulsive activity in persons with epilepsy.
Keywords: SNE; adenosine; field excitatory postsynaptic potentials; hippocampal slices; seizure.
Copyright © 2021 Amoateng, Tagoe, Karikari, Kukuia, Osei-Safo, Woode, Frenguelli and Kombian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abel C., Busia K. (2005). An exploratory ethnobotanical study of the practice of herbal medicine by the Akan peoples of Ghana. Altern. Med. Rev. 10, 112. - PubMed
-
- Adjei P. (2017). Traditional medicine in the management of epilepsy: a global approach. London, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, Vol. 165, 162–164.
-
- Adjei S., Amoateng P., Osei-Safo D., Sasu C., N’guessan B. B., Addo P., et al. (2014b). Sub-acute toxicity of a hydro-ethanolic whole plant extract of Synedrella nodiflora (L) Gaertn in rats. Int. J. Green Pharm. 8, 271–275. 10.4103/0973-8258.142695 - DOI
-
- Adjei S., Amoateng P., Osei-Safo D., Ahedor B., N’guessan B., Addo P., et al. (2014a). Biochemical and haematological changes following an acute toxicity study of a hydro-ethanolic whole plant extract of Synedrella nodiflora (L) Gaertn in male Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Med. Biomed. Sci. 3, 31–37. 10.4314/jmbs.v3i1.5 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

