Inhibition of TLR4/MAPKs Pathway Contributes to the Protection of Salvianolic Acid A Against Lipotoxicity-Induced Myocardial Damage in Cardiomyocytes and Obese Mice
- PMID: 33762947
- PMCID: PMC7982403
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.627123
Inhibition of TLR4/MAPKs Pathway Contributes to the Protection of Salvianolic Acid A Against Lipotoxicity-Induced Myocardial Damage in Cardiomyocytes and Obese Mice
Abstract
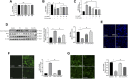
The occurrence of lipotoxicity during obesity-associated cardiomyopathy is detrimental to health. Salvianolic acid A (SAA), a natural polyphenol extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen in China), is known to be cardioprotective. However, its clinical benefits against obesity-associated cardiomyocyte injuries are unclear. This study aimed at evaluating the protective effects of SAA against lipotoxicity-induced myocardial injury and its underlying mechanisms in high fat diet (HFD)-fed mice and in palmitate-treated cardiomyocyte cells (H9c2). Our analysis of aspartate aminotransferase and creatine kinase isoenzyme-MB (CM-KB) levels revealed that SAA significantly reversed HFD-induced myocardium morphological changes and improved myocardial damage. Salvianolic acid A pretreatment ameliorated palmitic acid-induced myocardial cell death and was accompanied by mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular reactive oxygen species improvement. Analysis of the underlying mechanisms showed that SAA reversed myocardial TLR4 induction in HFD-fed mice and H9c2 cells. Palmitic acid-induced cell death was significantly reversed by CLI-95, a specific TLR4 inhibitor. TLR4 activation by LPS significantly suppressed SAA-mediated lipotoxicity protection. Additionally, SAA inhibited lipotoxicity-mediated expression of TLR4 target genes, including MyD88 and p-JNK/MAPK in HFD-fed mice and H9c2 cells. However, SAA did not exert any effect on palmitic acid-induced SIRT1 suppression and p-AMPK induction. In conclusion, our data shows that SAA protects against lipotoxicity-induced myocardial damage through a TLR4/MAPKs mediated mechanism.
Keywords: MAPKs; TLR4; lipotoxicity; myocardial injury; salvianolic acid A.
Copyright © 2021 Yang, Chen, Yan, Xu, Wu, Pi, Liu, Chai, Li and Dou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Dou X., Ding Q., Lai S., Jiang F., Song Q., Zhao X., et al. (2020). Salidroside alleviates lipotoxicity-induced cell death through inhibition of TLR4/MAPKs pathway, and independently of AMPK and autophagy in AML-12 mouse hepatocytes. J. Funct. Foods 65. 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103691 - DOI
-
- Gélinas R., Mailleux F., Dontaine J., Bultot L., Demeulder B., Ginion A., et al. (2018). Bertrand bouchard, christine des rosiers, benoit viollet, kei sakamoto, jean-luc balligand, jean-louis vanoverschelde, christophe beauloye, sandrine horman, luc BertrandAMPK activation counteracts cardiac hypertrophy by reducing O- GlcNAcylation. Nat. Commun. 9, 374. 10.1038/s41467-017-02795-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

