Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemic Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis
- PMID: 33763013
- PMCID: PMC7982901
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.619043
Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemic Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis
Abstract
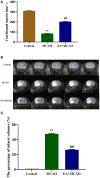
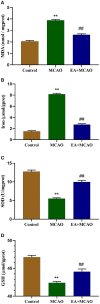
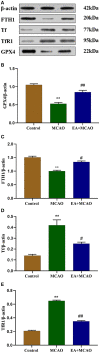
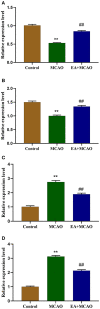
Background: Our previous study found that electroacupuncture (EA) can promote the recovery of neurological functions, reduce the volume of cerebral infarction, and protect the neurovascular unit in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) rats. Some studies have shown that ferroptosis is closely related to ischemic stroke; however, whether EA plays a protective role by regulating ferroptosis is unknown. Objective: We aimed to investigate the inhibitory effects of EA on ferroptosis in MCAO rats. Methods: We used 36 adult male Sprague-Dawley rats in this study. MCAO rats were established according to the Zea method and treated with EA at a continuous wave of 2/100 Hz and ~2-4 V for 30 min for 7 consecutive days. We analyzed the coordinated motor deficit and volume of cerebral infarction in vivo through 9.4-tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Then, the ischemic brain tissue was isolated and the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), and iron were determined. Western blotting and real-time quantitative PCR were performed to evaluate the expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), transferrin (Tf), transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1), and ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1). To confirm the results, we used a transmission electron microscope to observe the mitochondrial morphology. Results: EA intervention significantly decreased the oxidative stress level and inhibited ferroptosis. EA significantly improved coordinated motor deficit (P < 0.01) and decreased cerebral infarct volume (P < 0.01) in the EA + MCAO group, compared with the MCAO group. EA downregulated the level of MDA (P < 0.01) and total iron (P < 0.01) and upregulated the level of SOD (P < 0.01) and GSH (P < 0.01) in the EA + MCAO group, compared with the MCAO group. EA increased the levels of GPX4 and GPX4 mRNA (P < 0.01) and FTH1 and FTH1 mRNA (P < 0.05, P < 0.01), whereas it decreased the levels of Tf and Tf mRNA (P < 0.05, P < 0.01) and TfR1 and TfR1 mRNA (P < 0.01) in the EA + MCAO group, compared with the MCAO group. EA also promoted the recovery of mitochondrial morphology according to the mitochondrial classification system for the ischemic cerebral tissue. Conclusion: Our results indicate that EA can inhibit ferroptosis by regulating oxidative stress and iron-related proteins, thus conferring protection against MCAO in a rat model.
Keywords: electroacupuncture; ferroptosis; iron homeostasis; ischemic stroke; mitochondrial.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Li, Dong and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

