Case Report: Ziprasidone induced neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- PMID: 33763203
- PMCID: PMC7953912
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.51094.1
Case Report: Ziprasidone induced neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Abstract
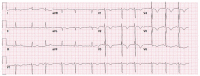
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a well-recognized neurologic emergency. It presents with classic features including hyperthermia, autonomic instability, muscle hypertonia, and mental status changes. The syndrome is potentially fatal and is associated with significant morbidity due to complications such as rhabdomyolysis, acute kidney injury, and ventricular arrhythmias due to the trans-cellular electrolyte shift. NMS is conventionally associated with the first-generation antipsychotic agents, however, has been described with the use of atypical and novel antipsychotics including Ziprasidone. A case of NMS with Ziprasidone use at the therapeutic dose is reported here.
Keywords: Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS); Neurologic emergency; Parkinson’s disease; Ziprasidone.
Copyright: © 2021 Sedhai YR et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources