Segmental analysis by speckle-tracking echocardiography of the left ventricle response to isoproterenol in male and female mice
- PMID: 33763310
- PMCID: PMC7958899
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.11085
Segmental analysis by speckle-tracking echocardiography of the left ventricle response to isoproterenol in male and female mice
Abstract
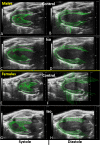
We studied by conventional and speckle-tracking echocardiography, the response of the left ventricle (LV) to a three-week continuous infusion of isoproterenol (Iso), a non-specific beta-adrenergic receptor agonist in male and female C57Bl6/J mice. Before and after Iso (30 mg/kg/day), we characterized LV morphology and function as well as global and segmental strain. We observed that Iso reduced LV ejection in both male (-8.7%) and female (-14.7%) mice. Several diastolic function parameters were negatively regulated in males and females such as E/A, E/E', isovolumetric relaxation time. Global longitudinal (GLS) and circumferential (GCS) strains were reduced by Iso in both sexes, GLS by 31% and GCS by about 20%. For the segmental LV analysis, we measured strain, strain rate, reverse strain rate, peak speckle displacement and peak speckle velocity in the parasternal long axis. We observed that radial strain of the LV posterior segments were more severely modulated by Iso than those of the anterior wall in males. In females, on the other hand, both posterior and anterior wall segments were negatively impacted by Iso. Longitudinal strain showed similar results to the radial strain for both sexes. Strain rate, on the other hand, was only moderately changed by Iso. Reverse strain rate measurements (an index of diastolic function) showed that posterior LV segments were negatively regulated by Iso. We then studied the animals 5 and 17 weeks after Iso treatment. Compared to control mice, LV dilation was still present in males. Ejection fraction was decreased in mice of both sex compared to control animals. Diastolic function parameters, on the other hand, were back to normal. Taken together, our study indicates that segmental strain analysis can identify LV regions that are more negatively affected by a cardiotoxic agent such as Iso. In addition, cessation of Iso was not accompanied with a complete restoration of cardiac function after four months.
Keywords: Adrenergic suractivation; Cardiac toxicity; Heart; Isoproterenol; Mouse; Sex differences; Speckle-tracking echocardiography; Strain; Takotsubo syndrome.
©2021 Walsh-Wilkinson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ali A, Redfors B, Lundgren J, Alkhoury J, Oras J, Gan LM, Omerovic E. Effects of pretreatment with cardiostimulants and beta-blockers on isoprenaline-induced takotsubo-like cardiac dysfunction in rats. International Journal of Cardiology. 2019;281:99–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.12.045. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

