Characteristic of Tumor Regrowth After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery and Outcomes of Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas
- PMID: 33763363
- PMCID: PMC7982800
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.627428
Characteristic of Tumor Regrowth After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery and Outcomes of Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to report the characteristic of tumor regrowth after gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS) and outcomes of repeat GKRS in nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas (NFPAs).
Design and methods: This retrospective study consisted of 369 NFPA patients treated with GKRS. The median age was 45.2 (range, 7.2-84.0) years. The median tumor volume was 3.5 (range, 0.1-44.3) cm3.
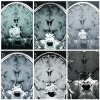
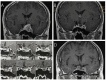
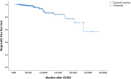
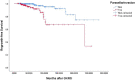
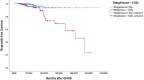
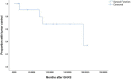
Results: Twenty-four patients (6.5%) were confirmed as regrowth after GKRS. The regrowth-free survivals were 100%, 98%, 97%, 86% and 77% at 1, 3, 5, 10 and 15 year, respectively. In multivariate analysis, parasellar invasion and margin dose (<12 Gy) were associated with tumor regrowth (hazard ratio [HR] = 3.125, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.318-7.410, p = 0.010 and HR = 3.359, 95% CI = 1.347-8.379, p = 0.009, respectively). The median time of regrowth was 86.1 (range, 23.2-236.0) months. Previous surgery was associated with tumor regrowth out of field (p = 0.033). Twelve patients underwent repeat GKRS, including regrowth in (n = 8) and out of field (n = 4). Tumor shrunk in seven patients (58.3%), remained stable in one (8.3%) and regrowth in four (33.3%) with a median repeat GKRS margin dose of 12 (range, 10.0-14.0) Gy. The actuarial tumor control rates were 100%, 90%, 90%, 68%, and 68% at 1, 3, 5, 10, and 15 years after repeat GKRS, respectively.
Conclusions: Parasellar invasion and tumor margin dose (<12 Gy) were independent risk factors for tumor regrowth after GKRS. Repeat GKRS might be effective on tumor control for selected patients. For regrowth in field due to relatively insufficient radiation dose, repeat GKRS might offer satisfactory tumor control. For regrowth out of field, preventing regrowth out of field was the key management. Sufficient target coverage and close follow-up might be helpful.
Keywords: aggressive; gamma knife; nonfunctioning; pituitary adenoma; radiosurgery; regrowth.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Wu, Quan, Fu, Cao, Li, Liang, Huang, Deng and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lucas JW, Bodach ME, Tumialan LM, Oyesiku NM, Patil CG, Litvack Z, et al. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guideline on Primary Management of Patients With Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas. Neurosurgery (2016) 79(4):E533–5. 10.1227/neu.0000000000001389 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sheehan J, Lee CC, Bodach ME, Tumialan LM, Oyesiku NM, Patil CG, et al. Congress of Neurological Surgeons Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guideline for the Management of Patients With Residual or Recurrent Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas. Neurosurgery (2016) 79(4):E539–40. 10.1227/neu.0000000000001385 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

